20 February 1403 12:10 pm
According to a new study, it seems that the Corona virus has other consequences and there is a connection between it and premature Alzheimer’s.
A new study shows that infection with the Corona virus, regardless of the risk of long -term cuvid, can significantly increase the risk of increased levels of brain proteins associated with premature Alzheimer’s disease.
Corona’s association with premature Alzheimer’s disease
The researchers found that the effect of the Corona virus on increased levels of amyloid beta proteins is equivalent to about 4 years of normal aging. This effect has been far more observed in people who were hospitalized due to the severity of the disease or had other risk factors such as hypertension.
According to the researchers, patients with Covid-19, even in mild or medium cases, are more likely to accumulate beta amyloid proteins in the brain than others. These proteins are known as one of the main causes of Alzheimer’s disease.
Despite the interesting findings of this study, there are important points to consider. This study is observable, and even if the Corona virus increases the risk of these biological markers, we cannot say that this is a specific effect of the SARS-COV-2 virus or other pathogens such as the flu can have a similar effect.
The authors of the study also acknowledged that the blood biological markers used in this study are relatively new and have not yet been fully accepted as clinical diagnostic tools. However, given the destructive effects of Alzheimer’s disease and many aspects of its unknown, such clues can be an important step towards a better understanding of the disease.
According to earlier findings, some infections have been associated with an increase in the risk of Alzheimer’s in a group of people, Eujin Duff, a neuroscientist at Imperial College in London, has introduced new results.

Duff says:
Our research shows that the Coved-19 may cause changes in the brain that can cause neurological diseases. We think these changes are caused by inflammation caused by infection, but the precise mechanism of the effect of this inflammation on the brain and amyloid protein changes have not yet been fully recognized.
“We also cannot determine how much the severity of Corona infection has to increase the risk of these diseases,” he said, noting that the Corona virus cannot be said to be definitely. »
Alzheimer’s is a complicated and progressive neurological disease that gradually analyzes people’s cognitive abilities and memory. It is the most common type of dementia, and according to the World Health Organization, more than 55 million people are affected by it.
According to the World Health Organization estimates, about 10 million new dementia cases are identified annually in the world, and it is estimated that about two -thirds of these are related to Alzheimer’s disease.


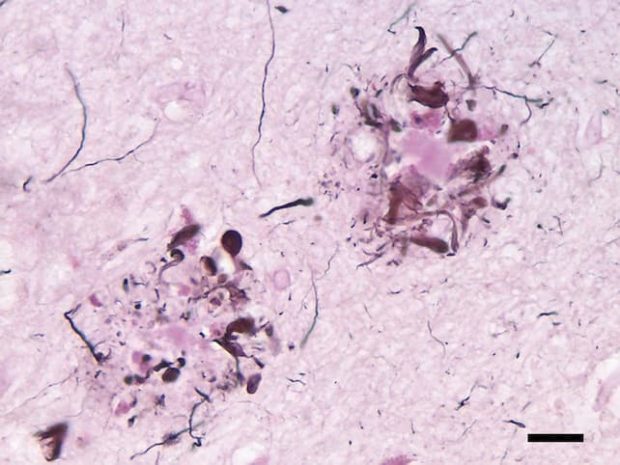
Alzheimer’s disease is still in a state of uncertainty. Researchers have so far focused on beta -amyloid plaques, but the exact role of these plaques and whether they cause the disease or a product of it is still unclear.
Beta amyloid proteins are naturally present in the body and perform many tasks. The problem begins when these proteins accumulate in the brain. These plaques are very close to Alzheimer’s disease. However, their exact role is not yet fully recognized.
The research team carefully examined the health data of 1252 participating persons at the age range of 46 to 80 years. The researchers compared the biological markers of the improved people from Corona to the markers of people who had similar characteristics but had no history of Corona infection.
The results of this study showed that people who had previously been infected with Corona are more likely to experience specific changes in their blood proteins. Previous studies have shown that these protein changes are associated with the accumulation of beta amyloid protein in the brain, which is one of the properties of Alzheimer’s disease.
(tagstotranslate) Alzheimer’s (T) Corona (T) Corona virus
RCO NEWS