13 June 1404 pm 11:51
What do you know about the mystery of sleep? Have you ever wondered why humans spend about a third of their lives in the world of dreams? We will answer these questions below.
Some estimates show that people spend an average of about one -third of their lives in sleep or trying to sleep. Sleep is a state of relaxation of the brain and body that is repeated regularly and is essential to maintaining physical and mental health. Join us at Gadget News to introduce you to the mystery of sleep more.
What do we know about the mystery of sleep?
When a person is in sleep, the body’s central temperature decreases. Heart rate and breathing slowly and overall metabolic activity drops about 10 %. Although the body may appear passive in sleep and the brain is less reactive than external stimuli, the fact is that the brain remains very active during sleep. In this situation, the brain performs important tasks such as repair and maintenance and strengthens neural communication between cells to optimize its function in waking up. Also, dreaming during sleep helps the process of organizing and stabilizing memories, as well as analyzing and storing information.

Sleep also allows the body to repair and repair damaged or analyzed cellular components. Many vital functions such as hormone secretion, tissue growth and muscle regeneration mainly occur during sleep. Also, the system of removal and toxins from the brain is more active during bedtime.
The natural cycle of sleep consists of two main stages, called Rapid Eye movements (REM) and sleep without RM. In each sleep cycle, the first three stages belong to non -RM sleep that start from light sleep and get deep sleep and eventually enter a RM sleep. During a usual period of sleep, one experiences four to six cycles of sleep, each lasting between 90 and 120 minutes. By repeating the cycles, the timing of the non -REM steps decreases and the share of the RM stage increases.
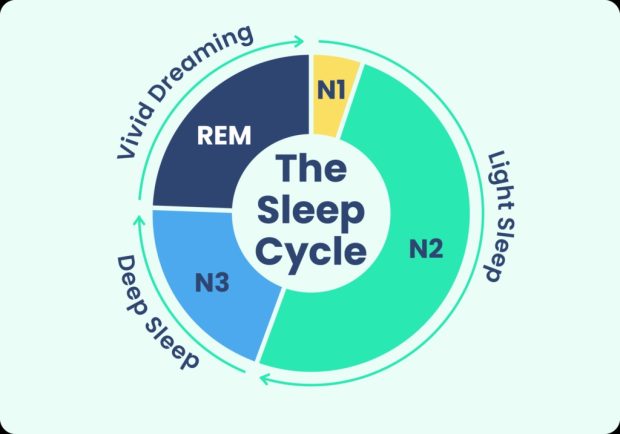

During sleep, the electrical waves of the brain show different patterns depending on the stages of the sleep cycle. The frequency of these waves is faster at the beginning of sleep and slows down as the sleep deepens.
The first stage of sleep is a non -RM stage called N1, which lasts between one and seven minutes. At this point, the muscles are calm and the person can wake up easily. After that, the N2 and N3 steps start from non -Rem sleep, where the body is more relaxed, the rate of breathing drops and the body temperature decreases. The N2 stage usually takes between 10 and 25 minutes, and the N3, which is a deep sleep, takes about 20 to 40 minutes.
The final stage is called the RM stage because in this phase the eyes move quickly as the eyelids are closed. At this point, the muscles have a temporary paralysis except the eye muscles. Much of the dreams occur in Rem’s sleep. About 25 % of the total bedtime is dedicated to Rem. This stage initially takes about 10 minutes but increases in subsequent cycles and may reach an hour.

The amount of sleep required for people varies depending on the age and personal conditions. Also, studies have shown that genetics can play a role in determining one’s need for adequate sleep. In the first months of life, infants usually sleep intermittently between 30 minutes to three hours and stay awake for about two hours to sleep again. Babies 4 to 12 months need about 12 to 16 hours of sleep over a 24 -hour interval, including daily naps. At this age, infants usually sleep in short intervals, but from about four to six months, they may have a continuous nighttime sleep between five and six hours, which is essential for brain and physical development.
Children need more sleep than adults because they are growing. During this period, daily naps are part of their sleep schedule. Children between 1 and 2 years of age to 11 to 14 hours of sleep, children 3 to 5 years to 10 to 13 hours and children 6 to 12 years need about 9 to 12 hours of sleep per day.
Adolescents, especially because of the important growth mutation they experience in their bodies and brains, should have at least 9 to 9.5 hours of sleep. As you enter puberty, changes in their body cycle occur, which makes them feel sleepy later. Unlike children, adolescents usually cannot sleep easily before 11pm, and it is more difficult for them to wake up in the morning.


Adults should have between 7 and 9 hours of sleep per day on average. As the age is old, the body’s rhythm is changed, so that people over the age of 60 tend to go to bed earlier and wake up sooner, while their sleep is not deep and uniform.
Insomnia is a disorder in which a person has difficulty sleeping, continuing sleep, or returning to sleep after waking up in the middle of the night, and as a result, he does not feel happy after waking up. If the sleep problem lasts only a few days, it is called acute insomnia. But if a person has at least three nights for three months or more per week, this condition is known as chronic insomnia.
The mystery of sleep; The reasons for insomnia
Many reasons can lead to insomnia, including stress, physical pain or anxiety. Inactivity, high consumption of caffeine, alcohol or tobacco can also disrupt sleep. Lack of regular sleep schedules, such as frequent changes in sleep or nap during the day, may also cause this disorder. Drugs that increase heart rate or reduce melatonin levels are also one of the factors. Also, genetics, some diseases and mental disorders can contribute to insomnia.


Creating a dark, calm environment and avoiding habits that disrupt sleep can be effective in removing acute insomnia. In chronic cases, consultation with a specialist is recommended to identify and treat the roots of the disorder. When one cannot have enough sleep, his or her physical and mental function is greatly reduced. The results are the results of fatigue, slow reaction, irritability, concentration weakness and memory disorder.
The consequences of lack of sleep
Lack of sleep reduces the reaction time and accuracy and increases the risk of accidents. In a study of medical staff with an irregular sleep pattern, the cognitive function of people deprived of sleep was similar to those whose blood alcohol was 0.05 %. In the United States, a driver with such a level of alcohol in the blood is known as dysfunction. Low -sleeping people may have micro -sleep; That is, for a few seconds to fall asleep, which is very dangerous if they are driving.
In the long run, lack of sleep leads to the formation of “sleep debt”, which has serious consequences for the brain and other body systems, including cardiovascular, hormonal, immune and nervous. Chronic insomnia can exacerbate existing diseases and increase the risk of stroke, type 2 diabetes, hypertension and heart disease. Also, insufficient sleep can increase appetite and cause overweight. Sleep deprived people are more prone to anxiety and depression. Of course, the two disorders themselves may also cause insomnia.


About sleep paralysis
Sleep paralysis is a state that one is unable to move or speak in the time of sleeping to wake up or vice versa, though he or she is aware of the environment. This may be associated with hallucinations or pressure on the chest and usually lasts for a few seconds to a few minutes, but in rare cases it will last up to 20 minutes. Despite the shortness of this experience, it often causes anxiety and disruption to sleep habits.
This condition, also known as muscle atony, occurs when the brain enters or out of bed. In this phase, the signals of the brain disable the muscles of the body so that the person does not move too much when dreaming. If the person wakes up in this case, the voluntary muscle control has not yet been recovered and will feel paralyzed.
The main cause of sleep paralysis is still unclear, but there are relationships between it and some mental disorders such as anxiety or post -traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Also, this phenomenon is more common in people with nuculps. Irregular patterns of sleep or some medications, such as hyperactivity medications, are also associated with increased risk of sleep paralysis. Estimates about the prevalence of sleep paralysis vary. Some estimates say that approximately 8 % of the world’s population during their lives develop at least once, and women have a little more than men.
(tagstotranslate) sleep
RCO NEWS