Disposable containers are dangerous behind its fascinating appearance and inappropriate use can threaten our health and the environment. I have been helping an experienced material expert and a nutritionist in writing this guide to tell us a series of practical tips on the world of disposable containers in a simple language. Reading the post makes you learn about a variety of plastic, herbal, paper and aluminum containers and learn what each container is right for, how to use it and what is the use and prohibition of each.
Comparison of disposable containers and their application
| Type of container | Recycling code and feature | Main Application | Benefits | Tips of Use (Consumption/Contraindications) |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Code 1, matte, flexible | Hot and fatty foods (stew, soup), yogurt | Good resistance to heat (up to 2 degrees), relatively safe | Authorized: Warm foods, microwaves (short heating). Prohibition: Cooking in microwave, straight flame. |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Code 1, transparent (fragile) or foam (unolite) | Transparent: Drink/cold food; Foam: hot foods (barbecue, chopped), tea | Transparent: cheap, style; Foam: Good thermal insulation | Authorized: Only cold (transparent), hot (foam) temporary (foam). Prohibition: Fluids/hot and fatty foods (toxic styrene release), microwave. |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Code 1, Transparent, Resistant (Water Bottle) | Bottle of mineral water, beverages, oil | Light, transparent, durable | Authorized: Cold liquids and room temperature. Prohibition: Hot/hot liquids, reuse (germ growth). |
| Polyethylene with high density (HDPE) | Code 1, Matter (Milk Bottle) | Bottle of milk, juice, yogurt | Resistant, relatively safe | Authorized: Cold liquids, food at normal temperatures. Prohibition: Hot liquids, cooking in microwave |
| Herbal containers | PLA, corn starch, breakable | Glasses, plates, spoon, food containers | Environmentally friendly (composting in compost), greater safety | Authorized: Hot and cold foods (depending on the quality). Prohibition: Very high heat (some types), require industrial compost for complete breakdown |
| Paper and cardboard | Paper/cardboard | Tea/coffee mugs, pizza boxes, potato dishes | Light, cheap, recyclable (if contaminated) | Authorized: Hot/cold drink, temporarily carry food. Prohibition: Very hot liquids, long -term maintenance of fatty foods (softening, non -recycled) |
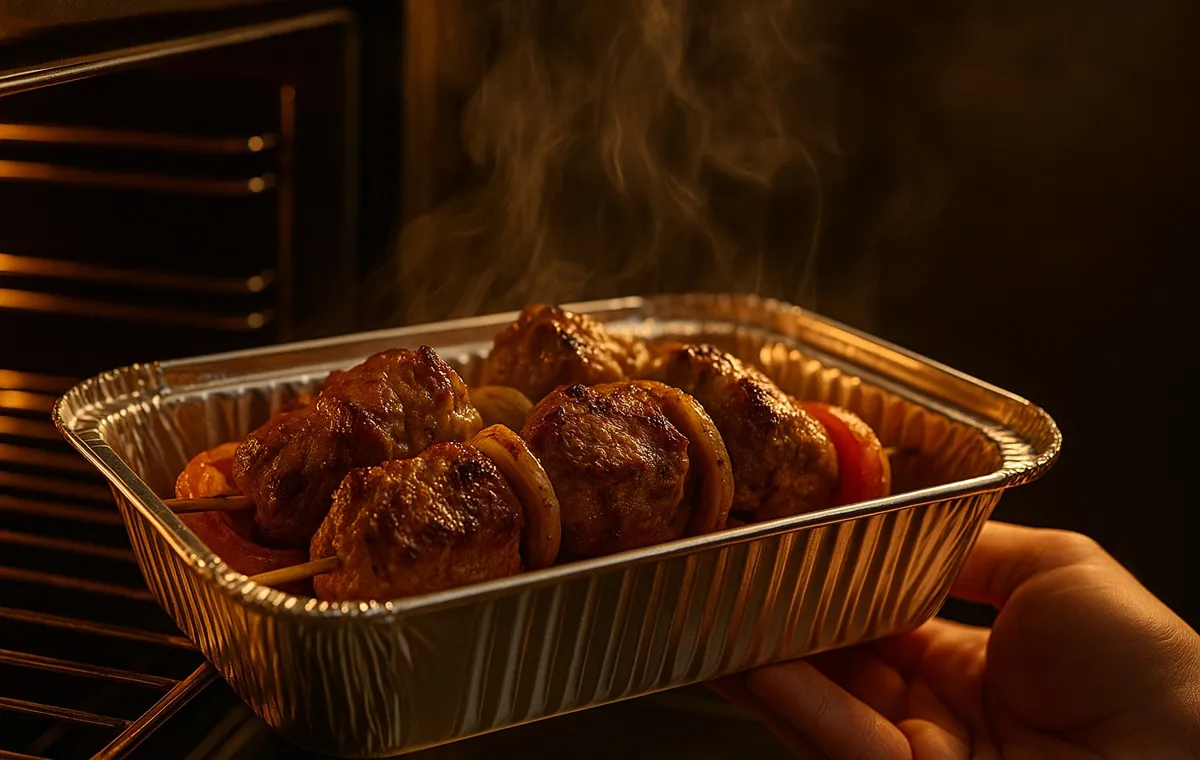
| Aluminum | Shiny, flexible (foil) | Stew, rice, barbecue, warm -up in the oven | High resistance to heat, retain heat, recyclable | Authorized: Warm foods, cooking in the oven. Prohibition: Long -term maintenance of acidic/salty materials, microwave (spark) |

191,900
182,300
Toman
Why is it important to know a disposable container?
Health is the first issue to answer this question. Some chemicals, especially in the face of heat or specific foods, can enter the food. Also, each container is designed for a specific type of food and temperature, and improper use causes the deformation of the container or even leakage.
If you care about the environment, you know the third reason you are better than me. We do not have compliments, disposable containers, due to the high volume of production and consumption, become environmentally friendly (our own waste).
Common types of disposable containers and their applications
In this section, we will be introduced to the most common types of disposable containers. Disposable containers of popular plastics and herbal and aluminum options each have their own features and applications.
Plastic disposable container
These are the most extensive and most common type of disposable containers. There are different types of each of which have their own identification code (usually a number inside a recycling triangle).
Polypropylene (PP – Code 1)
They are usually more opaque, are a little flexible, and are one of the most common containers for packing hot foods, such as stew, soup, and restaurant foods. They can also be used as yogurt, butter and bottle. The advantage is considered to be good resistance to heat because they twist the temperature of 0 to 2 degrees Celsius and are relatively safe in contact with food.
- Authorized use: The best option for hot and fatty foods. Can be used for a short time in the microwave (for warming, not cooking)
- Contraindications: It is not recommended for long -term storage of very hot or fatty foods. Avoid placing them on the direct flame or in the oven.
Polystyrene (PS – Code 2)
These categories of containers have two main types; The first category is transparent, in which they call ordinary polystyrene. Frame and transparent is their main feature, and if we want to give a precise example, we have to put hand on minerals or salad containers. The second category is disposable foam containers (EPS -ionolite). Fully lightweight and heat insulation. You can usually see them for packing rice and barbecue or as a cup of tea.
- Authorized use: Transparent samples are cold drinks and cold foods (salads, fruits) and foam samples are used to temporarily carry hot foods due to the thermal insulation properties.
- Contraindications: Transparent polystyrene containers should not be used for hot liquids or hot foods (especially fatty foods) because it releases toxic monomers (Styrene), which is harmful to health. The foam sample is not suitable for long -term storage of fatty and hot foods and should not be in the microwave because they are extremely sensitive to heat and melt.
Polyethylene Terraphy (PET – Code 1)
It is transparent and durable and is commonly used in mineral water bottles and soda. You see them as a bottle of mineral water, drinks and liquid oil and are less used as food containers, except in specific cases. If we want to list their benefits, we will come to these three; Light, transparent, impact resistant.
- Authorized use: Only for cold liquids and at room temperature.
- Contraindications: Do not use hot or hot liquids at all! Release these containers in the face of heat, harmful chemicals. They are not recommended for reuse (re -filling), as germs may grow in the inner grooves of the container.
High density polyethylene (HDPE – Code 1)
Their appearance is more opaque than PET and is commonly used as milk bottles or detergent containers. Sometimes they are used in the form of juice and yogurt containers. The first positive point of this type of disposable container is its high resistance and the next positive rating when we know they are relatively safe.
- Authorized use: For cold liquids and some food at normal temperatures.
- Contraindications: Microwave is not recommended for hot or cooking liquids.


Dummary
Usually, the PLA means polylactide. This mark means the container made of corn starch and reports that the container is renewable. They may look like plastic, but they are generally more matte or slightly coded. You see a disposable container mostly in the form of glass, plate, spoon, fork and food containers because it is a good option for people who care about the environment. Stay between ourselves, this type of disposable container releases less chemicals and breaks down only in appropriate conditions (industrial compost) and returns to nature.
- Authorized use: For hot and cold foods, depending on the type and quality of construction (they are also resistant to high temperatures).
- Contraindications: They may be less resistant to very high heat (such as directly on the flame). Some of them require special industrial compost conditions to break down and are not easily decomposed in nature. Before buying, look at the “compost” or “biodegradable” label.


Dummy
It is easy to identify because they are made of paper or cardboard. As a glass of tea and coffee, pizza boxes, fried potatoes, or ready -made food packaging dishes. Have many benefits; They are lightweight and cheap and can be recycled if they are not covered with plastic layer or their layer is detachable. Overall, they are relatively safe for food.
- Authorized use: Paper cups are suitable for hot and cold drinks (usually they have a thin polyethylene coating to prevent fluid leakage). As a pizza box and fried potatoes are popular.
- Contraindications: Fatty foods are not recommended for very hot fluids or long -term storage because they may soften or damage their coating layer. Pizza cardboard and other fatty foods are usually recyclable due to oil impregnated.


Aluminum container
They are made of glossy and flexible aluminum and are used as stews, rice, barbecue and ready -made foods to warm the oven. Aluminum foil falls into the same category. In general, they are highly resistant to heat and can be used in the oven or on the indirect flame. They maintain the heat well and they are highly recycled.
- Authorized use: Ideal for warm and cooking foods in the oven.
- Contraindications: It is not recommended for long -term storage of acidic or salty foods because aluminum can react with these ingredients and enter the food. It should never be in the microwave because it causes spark and damage to the device. Avoid scratching their inner surface with a metal spoon so that the protective layer does not disappear.

Golden Tips to use a disposable container
The disposable container has a birth certificate, which is seen as a series of code and number on the product. The recycling code (number inside the triangle) and descriptions on the container provide important information about the type of plastic.
Most of all, you should be careful about heat and fat because these two factors are the main enemy of health in disposable plastic containers. The hotter and greasy the food is, the more likely the leak is to leak in plastic.
If you have to use disposable containers for hot food, polypropylene (PP-code 2) and aluminum are the best options. Polystyrene containers (PS – Code 2), especially transparent and foam samples, are the worst choices for hot and fatty foods and should not be used as far as possible.
Do not re -fill the mineral water bottle (PET – Code 1) as they are designed for one consumption. Re -filling them causes the growth of bacteria and releases chemicals, especially in warm air.
Forget the washing and reuse because they are not designed for this, and washing can eliminate the protective layers and help the growth of germs. Use glass, porcelain, metal or stainless steel containers to store and carry food as much as possible. Herbal containers are also better environmental options. After proper use, properly separate the recyclable containers and place it in a recycling trash.
Source: DigiKala Meg


RCO NEWS