Three AI researchers at Zurich University of Technology, Switzerland, developed an AI-based image processing model to solve Google’s reCAPTCHA v2 human testing system.
These three researchers, Andreas Pelzner, Tobias Vantobel and Roger Wattenhofer, were able to modify the YOLO image processing model and achieve a new model that can solve Google’s CAPTCHA every time.
In recent decades, website administrators around the world used various methods to prevent the intrusion of robots and the occurrence of problems on websites; One such method is the fully automated general Turing test for distinguishing between computers and humans, known as CAPTCHA.
In 2007, Google released its own version with the latest update called reCAPTCHA v2. Like other CAPTCHAs, Google requires the user to click on the desired image to pass.
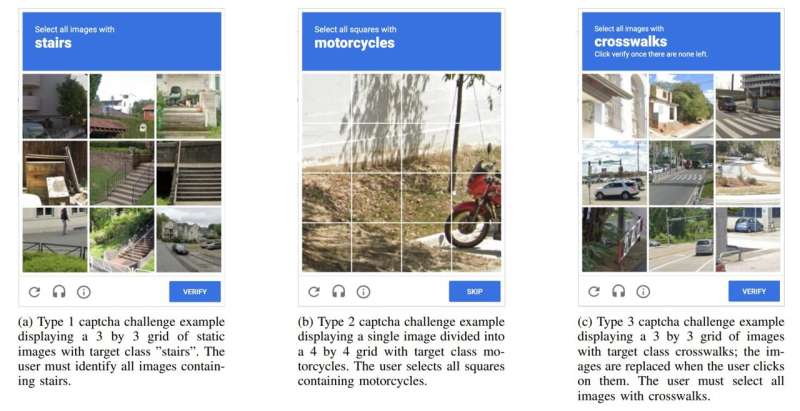
In a new attempt to break CAPTCHA, the team of researchers realized that it doesn’t take much effort to pass this barrier!
This was done by modifying the YOLO model to recognize objects commonly used by reCAPTCHA v2, such as cars, bridges, and traffic lights, and then training it on thousands of photos of the same type of objects.
Testing showed that the model does not need to be 100% accurate because reCAPTCHA v2, like other CAPTCHAs, allows for multiple attempts. The researchers found that even if the new model failed the first images, it would pass the second puzzle.
Further tests of the model showed that it can fool even more complex CAPTCHAs. This finding will undoubtedly lead to new research to create CAPTCHAs that cannot be fooled by an artificial intelligence system.
RCO NEWS















