Last year has been a turning point in biology advances, from new genetic discoveries to developing innovative therapies and progress in biological technologies. This year, the researchers were able to expand the boundaries of biological knowledge using artificial intelligence, genome editing and stem cell research. Here’s a look at biology in the year we left.
According to RCO News Agency, In the year we left, biologists used artificial intelligence to discovering molecules and brain and challenging the long -standing assumptions of the immune system (RNA).
Many types of discoveries can be amazing and happy, but few findings are more exciting than canceled hypotheses that scientists sometimes randomly.
Biologists, for example, have assumed that it was regulating its immune system without our brain intervention. But in the past year, they discovered that a neurotransmitter in the brain stem raises and lower the levels of inflammatory molecules, and this discovery was not done in a laboratory with specialization in immunology or immunology, but a laboratory with specialty in taste. Perhaps the need to change the view to make this discovery.
Scientists have made a number of other important progress this year in our essential understanding of how life works. New tools, especially artificial intelligence, are integrated into biology and cause discoveries. Researchers are creatively examining various ways by which multi -cells can evolve, including in some cases as to why evolution has not happened. Scientists also understand how small molecular changes have changed the face of modern evolution and biology.
Biologists get acquainted with the revolution of artificial intelligence
In year 4, it was difficult to spend a week without the publication of a new article related to Alphafold 2 (Alphafold۲) by Deep Madam from Google’s subsidiaries. Alfafold is a neural network that can predict the 3D structure of a folded protein from its one -dimensional filament of its amino acid molecules.
For example, in the discovery of the drug, biologists used it to identify new drug targets and psychotropic molecules. In the basic sciences, Alfafold 2 helped researchers to examine the viral evolution and discover a protein that attaches sperm to the egg. These growing advances showed a fundamental change in the relationship between biology and computer science.
“This changes structural biology in many positive ways,” says Paul Adams from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. This only makes this exciting field more exciting.
Why is Alpha Fold 2 important?
Proteins are essential molecules in the body of living things and their 3D structure plays a key role in their performance. Knowing the exact shape of a protein can be helpful in treating diseases, designing new drugs, better understanding of cellular biology, and artificial protein engineering. Prior to the development of alphabold, the researchers used methods such as X-ray crystallography and chryo-electron microscopy, which was very cost-effective and time consuming. Alpha Fold can predict the structure of proteins carefully within a few hours.

In May, the Alpha Fold 2 artificial intelligence system was also released, which predicts the form of proteins when interacting with other molecules. Then, in October, the Nobel Prize for Chemistry to John M. Jumper and Demis Hassabis of Google Dipmand as the creators of Alfafold 2 and David Baker from the University of Washington, a revolution in protein design was awarded.
Central moments in evolution: How did we get here?
This is one of the favorite questions of biologists. They tend to pursue the origin of life at an important moment in the history of evolution, and in the past year, they progressed in understanding how life begins as we know.
An interdisciplinary group used the latest phylogenic methods using genes and genomes to build evolutionary trees to track all modern life to our common ancestors. Scientists think that everything that is alive today derives from an ancient ancient cell named Luca, which stands for the phrase “last global common ancestry”. Luka was the first creature to have all the characteristics of a living cell and is the ancestor of all bacteria and eukaryotes. This cell has not been discovered directly.

Researchers’ innovation was in a way that evaluated the likelihood of each of the thousands of genes in Luka. The study showed that Luca is an amazing and complex cell that metabolizes hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide, has an elementary immune system, and is likely to live in a microbial ecosystem that is the only survivor. The study also determined Luka dating back about 1.5 billion years ago, older than the researchers thought.
Luka was the first creature to have all the characteristics of a living cell and is the ancestor of all bacteria and eukaryotes.
Another central moment, or better, a set of these moments, was the multi -cell evolution that happened not once but at least five times and possibly more. Carl Simpson, biologist, followed the emergence of multi -cell animal in the period of Earth’s history when the frozen planet was. Another study asked why bacteria and other prokaryotic cells could not evolve into complex multi -cell life. The answer can reach an evolutionary process called genetic drift.
Bacteria have created simple multi -cell shapes such as life as a colony, but their ancient versions never did it. In the past year, the researchers found that squeezing ancient cells could force them to form multi -cell colony and structural -like tissues.
In China, scientists also discovered fossils of multicolored eukaryotes dating back to 1.5 billion years ago, and this timetable would be the formation of multicolored eukaryotes of about 5 million years.
Inhumane mind and perception
Scientists are fanatical in understanding the world in a particular way. We see, hear with the eyes, and with a complex body we think of a miraculous way for billions of cells. Other creatures also feel, understand and respond to their environment, but they are difficult to imagine. In the past year, biologists encouraged us to open our minds.
In April, a group of biologists, cognitive scientists and philosophers signed a declaration that expands scientific support for “extraordinary awareness” to a broader set of animals, including insects, crabs, octopus, fish, reptiles and amphibians. These extremely vigilant creatures have the capacity to experience emotions such as pain or pleasure or hunger, but do not necessarily experience more complex mental states such as self -awareness.

Plants are not aware by themselves, but sometimes they need calculations. Research has shown that European beech trees can feel the longest day of the year. Every year, the trees coordinate their reproduction in a landscape called masting every year, from England to Italy, such as clockwise. Ecologists analyzed the data of more than 5 years to show that the rashes consider the event time until the summer revolution and the peak of the day’s light. Another study of the perception in the weeds. They appear to use air spaces between their cells to disperse light and create a gradient from light to low to pursue light during growth.
In the past year, the researchers also discovered that single -celled bacteria could feel the change in seasons. Simple day -to -day hours can trace the short day as they approach the winter and allow them to prepare for the colder weather, even if that winter reaches several generations later.
This is a world of Aran and we only live there
The Aran molecule has been less than a DNA since its discovery. This is a single -stringed, unassuming, and only messenger. But Research has become increasingly important that Aran is more important to life than we think. Most of the so -called non -forming parts of the genome are actually transcribed in the form of aran’s molecules that play non -messenger roles in cells such as regulating gene expression. A new view is emerging that states that many important and dynamic genome processes may be performed through Aran. The concept was strengthened by the Nobel Committee, which awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine to researchers who discovered microralna. These short molecules make it possible to regulate a gene that is the basis of complex and multi -cell life. The Nobel Nobel Committee awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine to Victor Ambers and Gary Rocon for the discovery of Micro Arani and its role in regulating the gene after transcription.
The increasing number of research also shows that Aran is a communication tool. Last year, for the first time, researchers found ancient cells that exchange non -destructive aran in extracellular vesicles and create a type of cellming system to share short and timely messages. The discovery confirmed that ancient cells, bacteria and eukaryotes could all exchange these Aran’s messages. It seems that transferring information to outside the cell may be one of Aran’s intrinsic roles.
In one of the strangest discoveries of last year, biologists have found a new form of a very strange Aran The flat circles were smaller than the virus and were nicknamed “Iblisk”. These strange arans live in bacteria that have learned our bowels and mouths. Still no one knows what their job is. “The world is full of new things and you find them when you start searching,” said North Carolina.
A look at the mind
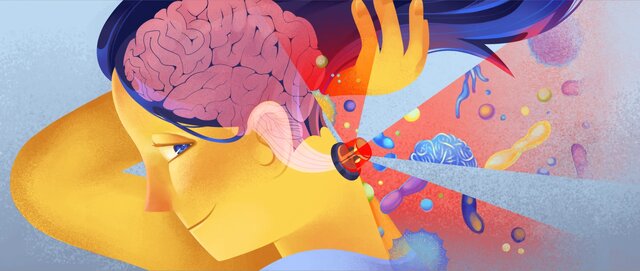
One of the most amazing discoveries last year has been the integration of the brain and body. Most immunologists have long thought that the immune system was regulated by itself. But for the first time, the researchers found a neural circuit in the brain stem that regulates the immune system. This circuit feels inflammatory molecules in the body and then raises or lower their surface to protect healthy tissues. This study shows increasing interest in structures that connect the mind and body, such as the vagus nerve or vagus, which is the longest brain nerve, which links the brain to the organs to guide the emotional response, and the spinal cord and the brain that covered the spinal cord and brain in a transparent fluid.
The world is full of new things and when you start exploring, you find them.Researchers have also progressed this year in understanding how thousands of neurons are active. “When we have experience, the neurons are activated in a certain order, as if they are hearing a melody on the piano,” says Daniel Bendor of the University of London. During rest and sleep, the hippocampus re -releases the sequence, but faster and potentially hundreds or thousands of times, causing electrical mosques. With rest, these sequences are likely to be stabilized in long -term memories.
On a very small scale, neuroscience scientists continue to study neurons to regenerate neurons. In the past year, Using artificial intelligence tools, Google scientists intertwined two images taken from one millimeter of the human brain, or a millionth of the whole structure to build an amazing 3D map. This section consists of approximately 2,000 neurons and 2 million synapses, accounting for 1.5 data. Also in the same case, The researchers first mapping the entire brain of vinegar. This brain is as much as a grain of sand and the largest brain to date has been fully mailed. The animal’s brain was mapping with 5,000 neurons compared to 2 billion neurons in the human brain. The next step, before mapping a complete human brain, is the mouse brain, which is about 5 times more neurons than the flies brain.

As you read, we have seen significant discoveries in the field of biology, and as expected, artificial intelligence has played a significant role in this field as in other fields of science. Given the increasing progress of the scientific fields, it is expected to be full of important biology discoveries, ranging from fundamental and genetic exploration to drug production and discovering new treatments.
The end of the message
(tagstotranslate) Biology (T) Neuroscience (T) Micro -RNA (T) Nobel Prize of Medicine
RCO NEWS


















