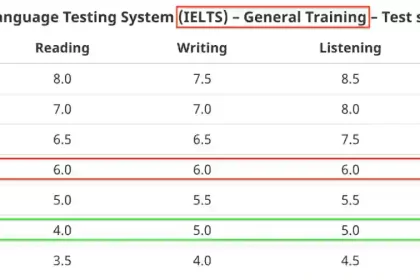
The Director General of the Office of the Geological Survey and Mineral Exploration Organization said that Iran is geographically in the world’s high -end belt. We face the phenomenon of 2nm dust.
According to RCO News Agency, Dr. Reza Shahbazi said today at the opening of the forty -third earthquake in the Geological Survey: “The story of the Sarakhun pipeline, which was damaged by a shake and we found that it was the second dangerous pipeline in the world’s oil transfer; It transmits oil from a wealthy region in the south of the country to the internal regions of the country, while facing natural risks.
He added: Iran is geographically in the world’s high -speed belt and is located in the dry areas, but thanks to the active technology and the unrest we have, roughness has created and caused the clouds to trap. It has led us to have a variety of climates, mines and diverse reserves, and of course a variety of risks in the country.
Shahbazi emphasized: This means that the same parameters that are the characteristics of wealth for us have made us see risky phenomena in the country.
The Director General of the Office of Geological Survey and Mining Exploration, emphasizing that Iran is the third most dangerous country in the world, stated: With every reference to the situation in Iran, Iran is one of the world’s most risky countries and in this high -risk country. People have always been looking for water and our habitats have been formed based on water.
He said that Iran has always been facing water shortages. We will consume renewable water, and we are currently consuming more than 5 % of renewable water.
“We consume more than 5 percent of water,” Shahbazi emphasized that if our consumption was head -to -head, we would not have something called subsidence, dust and drought in the country. Of course, the countries around us are also involved in this issue, and we live in a world that is currently exporting pulses to us. All of this is due to an increase in global temperature.
According to global reports, people who are currently between the ages of 1 and 2 have only faced a degree of temperature change, and what would happen if you reach 2 to 5 degrees in the next 5 years.
Referring to some global hazards due to climate change, Shahbazi noted: Today, potatoes are planted in Grland and there is no ice and all this is due to an increase in temperature. The world goes to warmer and increase carbon dioxide.
“We experience a warmer and drier world with more events, meaning that at once, 5 mm of rainfall occurs and to Suddenly Qeshm experiences 2 mm of rainfall, while we are completely dry.
He emphasized that developed countries have only 5 % of dry climates, and only 5 % of the population lives in these areas, and 5 % of the US residents live on the coast and 2 percent settled in the center of the country.
Shahbazi said the trend of earthquakes is almost constant, and in Iran we experience almost one earthquake with more than 2 magnitude every 5 years, but gradually the events in which climate are influential, such as floods, floods, and more and more, and 5 %. One of the events we are unable to manage when we encounter it is increasing in the world.
“We live in an area where we have two main risks, namely earthquakes and water -related challenges,” he said. This causes migration. Immigration can have a variety of reasons, and we see that immigration to the north of the country is starting.
Referring to the construction in the north of the country, he said: In the flood of April 6, I saw four areas that were falling on the road to Khorramabad, while nothing happened in the area five years before. It was and after five years of disaster, these infrastructure arose.
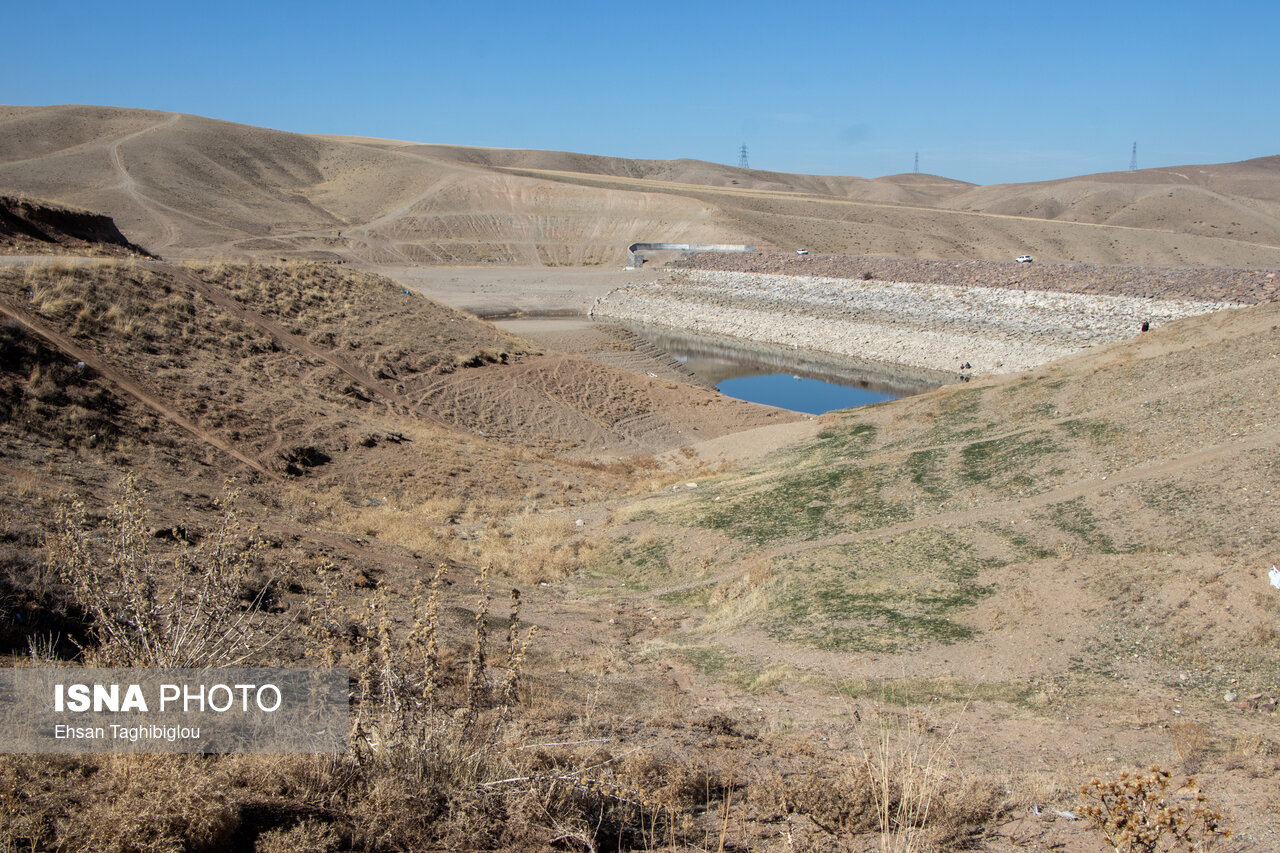
Shahbazi continued: Iran has entered a continuous drought since year 6 and all water levels have been dropped. We drilled more and more water was harvested until year 3, but more wells were drilled and we harvested less water, which was called subsidence and disrupted the water cycle.
The researcher said: Between the ages of 1 and 2, the area of subsidence zones has doubled, ie, we have 5,000 square meters of subsidence, and the rate is likely to be lower and lower in the future, because the underground no longer remains blue. .
Shahbazi described the occurrence of nanometer dust as one of the other challenges and said: There are 2,000 square kilometers of dust production centers around Iran, but what to do with 2nm particles. The information station information at Ferdis Karaj Bridge on November 5 shows the size of 2nm particles.
The end of the message
(tagstotranslate) land subsidence (T) Earth Science Congress (T) drought (T) Geological Survey
RCO NEWS