The liver is one of the vital organs of the body that does its job quietly and may not signal until it is severely damaged. Perhaps this is why hepatitis is called “silent” disease. Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver, which can occur due to various factors. The disease is seen both in contagious viral types and can be caused by non -productive causes such as alcohol consumption or autoimmune diseases. But what is hepatitis and why is it so attention? The fact is that viral hepatitis is one of the most important health problems in the world. For example, hepatitis B alone kills more than one million people every year in the world. These shocking statistics show how critical it is to get acquainted with hepatitis and its prevention and treatment. The following is a hepatitis and how it is transmitted, it examines its various types (especially hepatitis B), symptoms of hepatitis, transmission, treatment, and differences between acute and chronic hepatitis.
Click to see this article with artificial intelligence!
What is hepatitis and how is it transmitted?
Hepatitis is called inflammation of the liver tissue. This inflammation can be caused by various factors; The most common cause of hepatitis in the world are hepatitis viruses, with five main types of A, B, C, D and E. Each of these viruses has a different way of transmission and severity of the disease.
Hepatitis transmission ways vary depending on the type of virus. Hepatitis A and E are mainly transmitted by the use of water or food contaminated to the virus (stool-7). In contrast, hepatitis B, C and D spread through blood and body fluids.
For example, what is hepatitis B and how is it transmitted? Hepatitis B is a viral liver infection that is transmitted through blood, body discharge and sexual contact. The virus can be transmitted from the mother to the infant during childbirth or spread through the common use of syringes and needles, infected blood transfusions, tattoos with non -conductor devices and unprotected sex. The good news is that daily calls (hands -on, kissing, shared use of food containers, etc.) do not convey hepatitis B or C; Therefore, regular association with the affected person is not risky. About hepatitis C is also the main path of blood transmission; For example, through a common syringe among injectable drug addicts or blood transfusions in the past (before accurate blood screening). Hepatitis C is less transmitted by sex, but if blood contact is possible.
Hepatitis D occurs only in people who have hepatitis B at the same time because it needs B virus to reproduce. For this reason, hepatitis B vaccine also prevents hepatitis D. Hepatitis A and E are most common in areas with poor hygiene and can be prevented by food and drinking water.

3,600,000
1,910,000
Toman

3,600,000
1,910,000
Toman
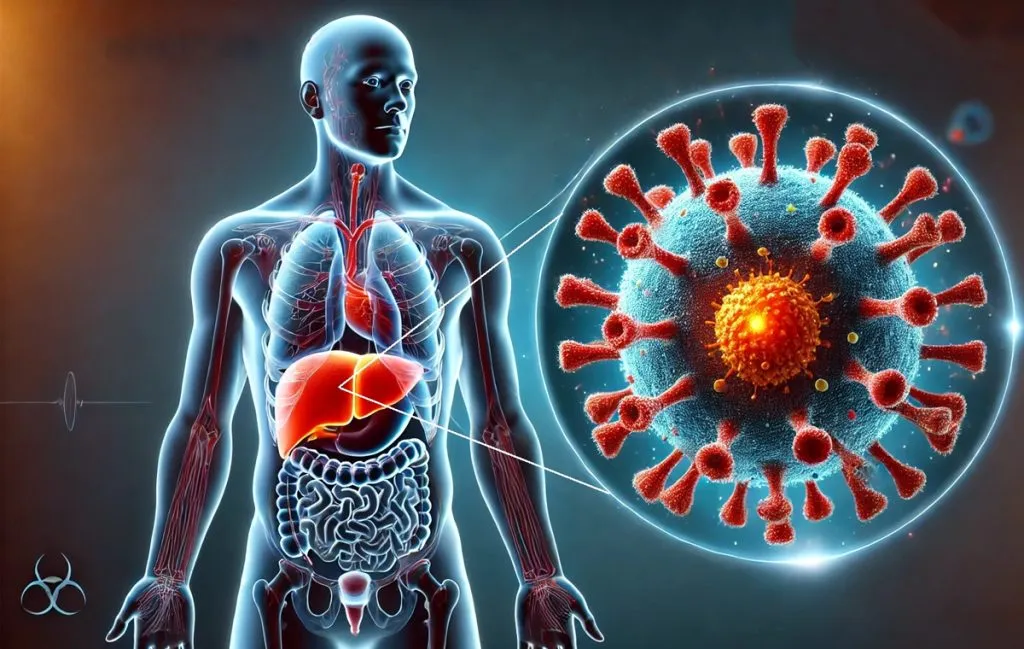
What is the cause of hepatitis?
The cause of hepatitis can be infectious or non -infectious. The most common causes of infectious hepatitis are hepatitis A, B, C, D, E viruses that we described earlier. In addition, some other viruses such as infectious mononucleosis (EBV) or cytomegalovirus (CMV) can also cause liver inflammation (hepatitis), although they are not named classic hepatitis.
In the case of non -infinite causes, excessive alcohol consumption is one of the most important causes of chronic hepatitis (alcoholic hepatitis) that can lead to cirrhosis. Taking certain medications or toxins can also damage the liver and cause drug hepatitis; For example, over -consumption of acetaminophen (paracetamol) can lead to severe acute hepatitis. Anti -cetic drugs, some antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and specific medicinal herbs in rare cases may cause liver inflammation.
Another important factor is autoimmune diseases. In hepatitis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the liver cells and causes chronic inflammation of the liver. The exact cause of this autoimmune is not fully known, but genetic and hormonal factors are involved and the disease is more common in young women. Hepatitis is not contagious and is classified as non -prizes of hepatitis. Lack of treatment can lead to liver or cirrhosis failure, but can be controlled by timely diagnosis and drug treatment.
Another factor is NAFLD, which occurs as a result of fat accumulation in the liver and can sometimes cause inflammation (non -alcoholic osteocheptitis). This is most commonly seen in obese or diabetic people and can advance to fibrosis and liver cirrhosis. Although non -alcoholic fatty liver falls into the category of chronic hepatitis, it often progresses and can be improved by modifying lifestyle (diet, exercise and weight loss).

183,000
149,000 Toman
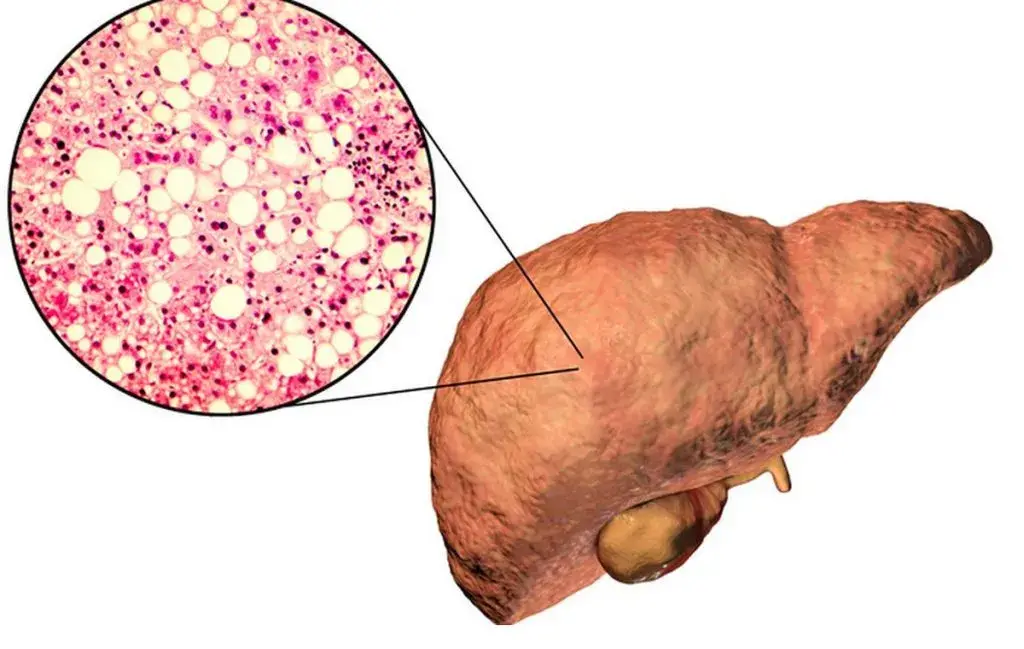
What is the most dangerous type of hepatitis?
When it comes to the most dangerous type of hepatitis, we need to determine what the risk criterion is. In terms of the severity of the disease, hepatitis D can be considered one of the most dangerous because it appears only in hepatitis B patients and can cause severe liver damage in the form of simultaneous infection. The rate of progress towards liver failure is high in simultaneous infection B and D. However, since hepatitis D cannot be published without the B virus, hepatitis B and C are the most dangerous on the world.
Hepatitis B is dangerous because it can become chronic and lead to cirrhosis (chronic inflammation and hardening of the liver tissue) or liver cancer. Statistics show that hepatitis B is the most common cause of cirrhosis and liver cancer in the world. As mentioned, the virus kills more than one million people in the world every year. Fortunately, there is an effective vaccine for preventing hepatitis B, which we will deal with later.
Hepatitis C is also a dangerous disease due to long -term complications. The virus usually leads to chronic infection and lasts “silent” for years until it can cause severe liver damage in late stages. There has been no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C, and this has raised much concern in the past. However, medical developments in recent years have transformed hepatitis C treatment; New drugs can fully cure more than 1 % of hepatitis C cases. So today there are new hopes for hepatitis C inhibition, though its timely diagnosis is still challenging. The following is a further introduction to the main types of hepatitis:
What is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a liver viral infection caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV). The virus can cause the disease in acute (short -term) or chronic (long -term) disease. Many people may have no symptoms in the acute phase of infection (especially children). But others, after a few weeks of virus arrival, develop symptoms such as jaundice and eyes (jaundice), severe fatigue, nausea, vomiting, bold urine and pain in the upper abdomen. These symptoms usually take a few weeks and then improve. In rare cases, acute hepatitis B can be so severe that it can lead to acute liver failure that is very serious.
The main problem occurs when the virus stays in the body and causes chronic infection. About 2 to 5 percent of adults with hepatitis B do not remove the virus from their body and reach chronic state. In chronic infection, there may be no specific symptoms for years, but the virus can damage the liver correctly. In the long run, chronic hepatitis B can cause cirrhosis (liver laziness) or liver cancer. These complications can be deadly. Hepatitis B is so common and risky that there are currently more than 5 million chronic carriers living in the world.
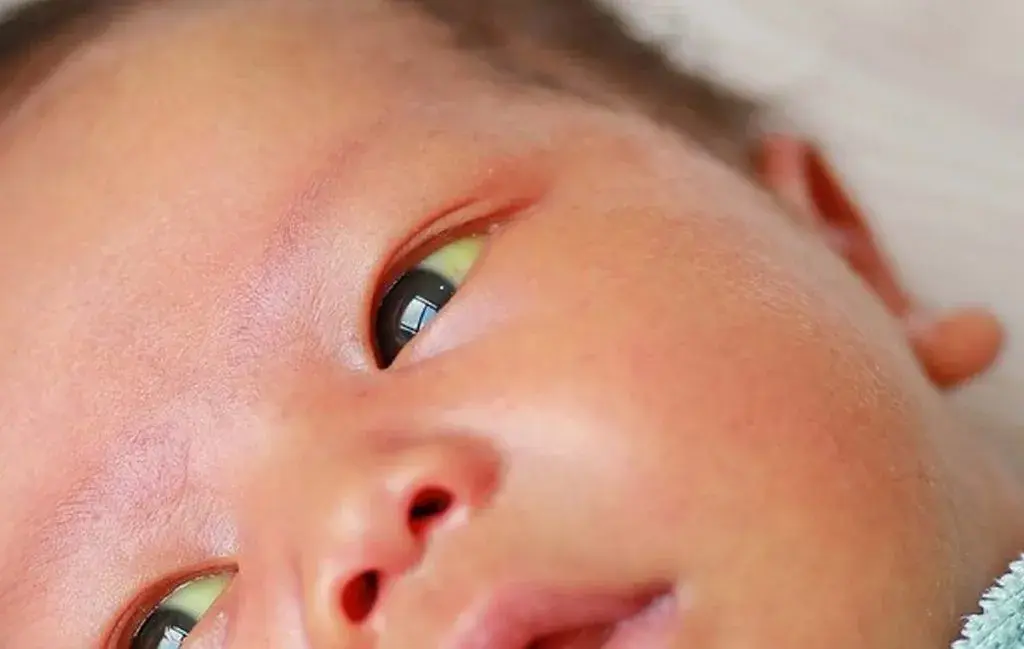

What is Hepatitis A?
Hepatitis A is a type of viral hepatitis A that is fortunate enough to have a relatively benign. Hepatitis A virus is transmitted to the affected person by consuming contaminated food or contaminated drinking water. The disease is most commonly seen in areas with low hygiene and in children. Symptoms of hepatitis A are usually mild and short -term and can include mild fever, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain especially in the upper and right (liver area), urination and jaundice of the eyes and skin. Unlike hepatitis B and C, infection with A virus does not become chronic and improves after weeks to several months. Almost all patients after recovery, the body becomes prolonged and immune to the virus for the rest of their lives. Although rare cases of severe hepatitis A or Fulminant (acute liver failure) have also been reported to be fatal, these are very low (less than half a percent). There is also an effective vaccine to prevent hepatitis A, especially for travelers to high prevalence or at risk.
What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is another liver viral infection caused by hepatitis C (HCV) virus. The virus is mainly transmitted through blood; For example, the use of joint syringes in addicts, tattoos or unhealthy piercings, blood transfusions or infected blood products (before the 1980s) have been important ways to spread. Hepatitis C sex transmission is less common than B, but may occur if they have ulcers and blood contact. Hepatitis C can appear acute or chronic, but most cases (about 1 %) become chronic infection. The important and dangerous thing about hepatitis C is that the infection usually goes off and irregular; Many patients have not noticed the virus in their bodies for years or even decades. During this time, the virus gradually damages the liver tissue and may cause cirrhosis or liver cancer after 2 to 5 years. If the symptoms of acute hepatitis C occur (which is rare) will be similar to other hepatitis: jaundice, fatigue, nausea, joint and abdominal pain, dark urine, etc., but most people do not have any specific symptoms in the acute phase.
The difference between acute and chronic hepatitis
- What is acute hepatitis? Fresh inflammation with a length of less than 6 months; It may be marked (jaundice, etc.) or inappropriate and often returns if the cause is resolved.
- What is chronic hepatitis? Stable inflammation for more than 6 months; Common in B and chronic are silent for years, but they raise late risks (fibrosis, cirrhosis, cancer).
The treatment is also different; Acute viral is usually supportive (except for special cases), but chronic requires antivirus treatment/prolonged follow -up. In the language of allegory: Acute is like “short storm” and chronic like “I don’t rain but long” that if it continues, floods.
Symptoms of hepatitis
Symptoms of hepatitis can vary depending on the type of virus and acute or chronic. Many viral hepatitis (especially hepatitis B and C) have no specific symptoms in the early stages. In general, in acute cases where the symptoms occur:
- The patient may experience a period of symptoms of symptoms or colds: Excessive fatigue, mild fever, nausea and vomiting, anorexia and muscle or joint pain and pain in the upper abdomen (liver site) may also be present.
- One of the most prominent symptoms of acute hepatitis is jaundice; That is, the yellowing of the skin and eyes caused by rising bilirubin in the blood due to liver dysfunction. Dark urine and pale stools are also classic symptoms associated with jaundice
- In some types of hepatitis A and E patients may develop diarrhea.
If hepatitis reaches advanced stage or liver failure (for example, in advanced cirrhosis), more severe symptoms appear; Including abdominal swelling and feet (due to fluid or ascite accumulation), gastrointestinal bleeding, decreased consciousness (due to liver encephalopathy) and severe weight loss. Such symptoms indicate serious liver damage and require immediate medical attention.
What are the symptoms of hepatitis B?
From completeness to the set of symptoms above. The latency period is usually 1 to 2 months. In the chronic type, there may not be a symptom for years and the first message may be abnormal blood tests or cirrhosis complications. Therefore, exposure to the rigor (injecting consumers, a history of nonstrill tattoos, high -risk sex, blood in the past, HBSAS positive infants) are more essential to screening.


What is Hepatitis Treatment?
Hepatitis treatment varies depending on the cause. In viral types, the goal is to treat the virus and to maintain liver function; In non -oral hepatitis, such as alcohol or drug -induced cases, it is improved by eliminating the stimulus and support care.
- Hepatitis A and E: They do not have specific treatment and often improve spontaneously. Rest, light nutrition, avoidance of alcohol and liver damaged drugs (such as high acetaminophen) and in rare cases are necessary.
- Hepatitis B: In the acute type, it is usually spontaneously resolved, but in chronic type of treatment with oral antiviral drugs such as tensophocovir and integrity to reduce the proliferation of the virus inhibition and progression to cirrhosis or cancer. There is no definitive cure at present and is usually long -term.
- Hepatitis C: Treatment with direct antivirus (DAA) such as Sophosbuvir or Daclasovir in more than 1 to 2 weeks in more than 1 % of patients.
- Hepatitis D: Effective treatment is limited; Sometimes it responds to interferon. The new Bolortide drug has shown good results, but the most effective way to prevent D is vaccination against B.
- Autoimimney hepatitis: Controlled with immunosuppressive drugs such as prednisone and azathioprine to inhibit inflammation.
- In cases of severe liver failure or injury, liver transplantation is the only salvation option.
In short, hepatitis Treatment varies from supportive care to antiviral treatment and ultimately liver transplantation, and its main purpose is to maintain liver health and prevent complications such as cirrhosis and cancer.
What is a Hepatitis Test?
Hepatitis test is a set of blood tests performed to diagnose the type of virus, the stage of illness and immunity. In hepatitis B there are three main indicators:
- HBSAG: Indicates active infection in the body.
- Anti-HBS (HBSAB): indicating the immunity against the virus (due to vaccine or recovery from previous infection).
- Anti-HBC (HBCAB): It shows that a person has been in contact with the virus in the past, but does not protect itself.
Alt, AST and blood bilirubin enzymes are also measured to assess inflammation or liver damage.
Overall, the hepatitis test helps the physician to determine the type of virus A, B, C, etc., to determine the acute or chronic infection and immunity.
What is a Hepatitis Vaccine?
I mean Hepatitis Vaccine Vaccines are made to prevent hepatitis Verros. Fortunately, very effective vaccines are available for two common types of hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
- The hepatitis B vaccine entered the neonatal vaccination program in Iran since the 1980s, and now all infants receive several doses of the vaccine at birth and in the following months. This vaccine provides long -term safety (at least 5 years or more) and prevents up to 1 % of hepatitis B. With the extensive vaccination, hepatitis B levels in new generations have fallen dramatically.
- The hepatitis A vaccine is also available and provides high safety. This vaccine is usually injected two times within a distance of 6 months and provides at least 2-5 years of immunity (and even lifetime in many people). In developed countries where public health is good, public vaccination is less need, but it is recommended for people who plan to travel to areas with high prevalence of hepatitis A or those with liver disease.
- For hepatitis C, there has been no effective vaccine so far. The HCV virus has challenged efforts to build vaccines due to its high genetic diversity and immune system volatile mechanisms. However, research is ongoing and several possible vaccines are underway clinical tests.
- In the case of hepatitis D, as mentioned, there is no separate vaccine, but the hepatitis B vaccine is the best protection against D. Because if a person is safe against B, he will not have D.
- A vaccine has been licensed and used for hepatitis E. The vaccine has not yet been widely released, but hepatitis E’s epidemic has been used in some areas. The most important way to prevent hepatitis E is to improve the quality of drinking water and dispose of sewage.
Frequently asked questions
What is hepatitis B and how is it transmitted?
HBV viral infection with acute to chronic spectrum; Transfer from blood and body fluids (childbirth, joint needle, non -protection tools, without protection). The vaccine has an effective and prevents from indirectly.
What is Hepatitis Auto Safety?
A chronic inflammation of the liver in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the liver. It is not contagious and managed with immune suppression drugs. Rapid diagnosis prevents progress to cirrhosis.
What is the Hepatitis B test for?
To detect the condition of the disease/immunity: HBsAg (active infection), anti-hbs (immunity), anti-Hbc (previous/current call). Along with liver enzymes and if needed, HBV DNA is evaluated and the need for treatment is evaluated.
What is Hepatitis in Blood Test?
A set of specific viral tests and liver markers is called the virus, immunity or liver damage. A precise interpretation is done with the physician.
What is the silent hepatitis?
The nickname B and C chronic, which has been impaired for years and slowly damages the liver. The importance of screening people at risk is precisely here.
What is Hepatitis E?
HEV virus, transmission like A (contaminated water/food), usually acute and self -confident. It can be more severe in pregnancy. The public vaccine is not available; Prevention with healthy water and food health.
RCO NEWS