Since time immemorial, maps have been a continuous human effort to depict the world.
It has been more than 5,000 years since mankind realized the importance of cartography and started designing and making maps. Early maps were used as a tool to record important places, teach the geography of a region, and war and political strategies. They covered small areas such as cities, trade routes, hunting areas, etc. and did not have a fixed orientation; For example, north was not always at the top of the map. Also, the early maps had little accuracy and in their design, art and painting were often preferred to geographic accuracy. Each period of the history of map writing reflects the priorities and technologies specific to its time and describes the way humans understand and interact with the world around them.
The evolution of cartography throughout history:
The beginning of the mapping process
Although a 25,000-year-old carved mammoth tusk in the Czech Republic appears to be the oldest known map; However, there are still many differences between archaeologists, geographers, cartographers, etc. on which one is considered a map or just a work of art left by the ancients.
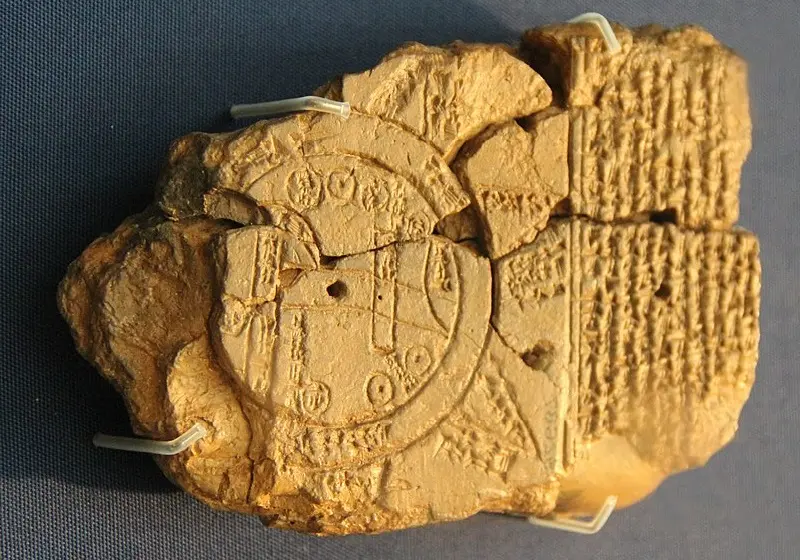
What cartographers accept as the oldest map is from the Babylonians. Babylonians drew simple designs on clay tablets. One of the remaining works of that era (4th to 12th century BC) and perhaps one of the first maps of the world, is a tablet that shows the world as a circle surrounded by water. This map is a reflection of the beliefs, beliefs and worldview of the people of Babylon and Mesopotamia.
After that, the Egyptians created maps to record land boundaries, and then the Chinese carved delicate croquis on silk.
Babylonian map tablet; Source: Wikimedia; Photographer: Gary Todd
Cartography in ancient times
Around 150 AD, the Greeks and Romans perfected the art of cartography. One of the most famous astronomers and cartographers of that era is “Claudius Ptolemy” (Ptolemy), who most likely lived in ancient Greece, the city of Alexandria located in Egypt. By discovering the latitude and longitude lines, he used mathematics to design and combine maps and wrote the treatise “Geography”. Ptolemy’s geography treatise is probably considered the first cartographic treatise and atlas of history, which depicts a large and integrated map with few details of the world of his time. This atlas has more accurate regional maps with more details and explanations. This work has had a significant impact on European and Islamic cartographers.
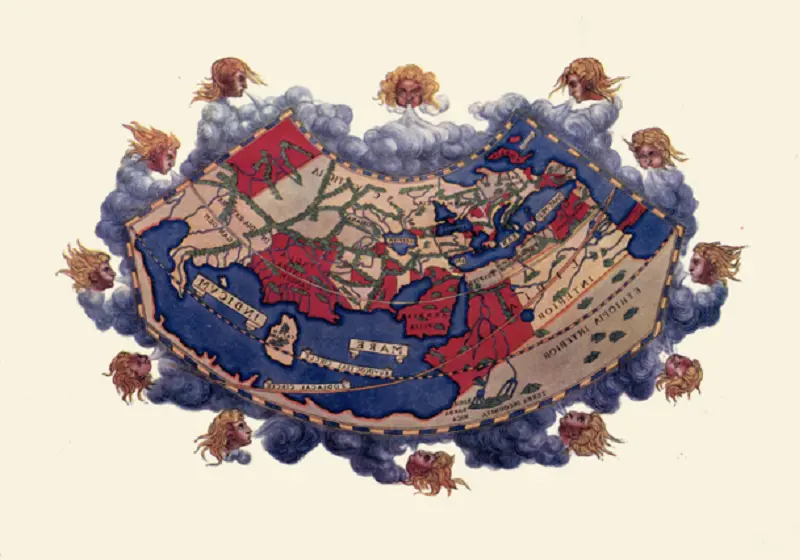
Ptolemy’s world map; Source: Wikimedia; Photographer: Margaret Bertha Synge
Cartography in the Middle Ages
In medieval Europe, there was little progress in cartography; Because the maps were dominated by the church and focused more on religious themes and reflected biblical interpretations. In the maps designed by the church, Jerusalem was placed in the center of the map and Asia above it, and the images were decorated with artistic elements such as angels, saints and imaginary creatures. At that time, due to the fanatical belief of the church that the earth is flat and not spherical, astronomers and cartographers were not able to publish the maps they had drawn from the real world with the help of astronomy. As a result of this, Europe has not had significant progress and achievements in this field; Of course, people like “Constantine of Antioch” (Constance of Hauteville), created Christian topographies that showed the earth as a flat plane and were accepted by the church; But until the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Renaissance, astronomers such as Galileo Galilei were not allowed to express the truth.
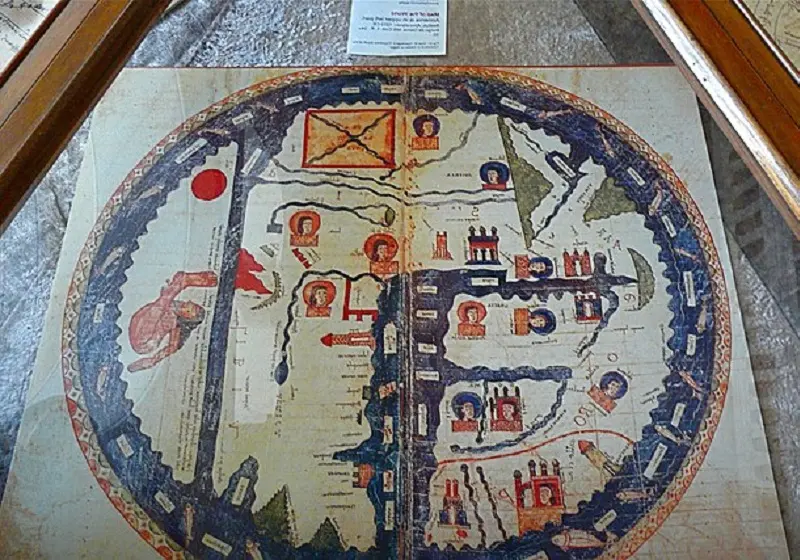

medieval world map; Source: Wikimedia; Photographer: Rita Willaert
Cartography in the sixth century Islamic world
During the period when medieval Europe used the science of cartography and geography in the service of Christian beliefs, the Islamic world was making significant progress in this field. Muslim scientists and geographers, following the methods of Ptolemy and using the knowledge and writings of explorers and traders who passed through the trade routes of the world, designed the world on paper. They provided more precise definitions of units of measurement and were able to calculate the circumference of lands and territories. Also, the Muslim cartographers of that era designed a complex system of peninsulas and vertical and horizontal lines of land division, which had a great impact on the quality and accuracy of cartography. Among the important geographers of that era is “Mohammed Sharif Idrisi”.
Idrisi had a lot of experience in walking and traveling and finally settled in Sicily island in the Mediterranean Sea for 16 years, in the court of King “Roger II” (Roger II of Sicily). write down This book was noticed by the king at that time; Tajai suggested that he use the silver of the royal court to make maps in this book to design the images of the regions that he has included in his treatise and add them to the pages.
The island of Sicily was the destination of many travelers, and Idrisi asked travelers, merchants, etc. about the lands where they lived to complete the details of his maps. Also, his association with the Christian kingdom provided him with significant information about other Christian countries of that time, such as France, England, Germany, and even the Scandinavian peninsula.
The book “Nazha Al-Mushtaq fi Akhtaraq al-Afaq” which is known as “The Book of Roger” in Europe; It was written about the seven climates in the 6th century of Hijri, it consists of 70 maps and it is the only geographical book that was written in that era. In this masterpiece, the natural features of the world to the information related to ethnic groups, the culture of the communities, the economic conditions of the territories and many other things are mentioned. Now the original version of the book, in Idrisi’s handwriting, is in the Hamburg National Museum.
This atlas, which has drawn the world as a sphere and divided it into 70 rectangular sections, wrote the following about the first climate:
This climate starts from the west side of the sea which is known as the dark sea and…
In this phrase, the meaning of “Bahr al-Daklamat” is a place where mankind has no knowledge of its end. People of that time, because they did not reach the end of the Atlantic Ocean, believed that there was no life behind it.

Hydrangea world map; Source: Wikimedia; Photographer: Unknown
Cartography during the Renaissance
Changes in Europe after the Middle Ages and during the Renaissance had a great impact on cartography and cartography. Before that, maps were very simple and drawn in black and white, where only coastlines, country borders, mountains, rivers and place names were recorded. The most advanced maps before this era were those that were colored by hand to make them look more beautiful and clear.
In 1440 AD, “Johannes Gutenberg” invented the printing press, and thus the production and printing of maps was removed from the monopoly of religious institutions. In 1492, “Christopher Columbus” discovered the American continent and thus the migration and travel to distant areas increased.
The industry of printing and publishing works by large publishing houses grew significantly and this development made the maps available to the general public and were no longer limited to the elite, the rich, the nobles and the royal family. In 1666, many institutions such as the “French Academy of Sciences” were established, and this led to an increase in students and the growth and prosperity of various sciences, including geography, astronomy, cartography, navigation, and the design of sea maps, etc.
In the late 18th century, thematic maps appeared, which were used to record a specific event; For example, we can refer to “the location of people with an infectious disease” or “the extent and extent of a natural event such as a flood.”
Renaissance world map; Source: Wikimedia; Photographer: Włodzimierz Juśkiewicz
Cartography in the modern era
With the passage of time and the progress of human understanding of the earth, mathematics and geography, maps became more complex and accurate, satellite systems and accurate mapping methods created a revolution in cartography, and maps are now very accurate and are designed and published for many natural and human phenomena.
Using modern satellite systems and advanced mapping techniques, today’s cartographers have been able to measure and map with high accuracy and stability. As a result of these developments, maps have become a vital part of almost all fields of human activity.
Modern maps use well-known representations, include precise geographic details, note specific subjects such as land elevation and sea depth, and prioritize clarity, function, and accuracy over ornamentation.
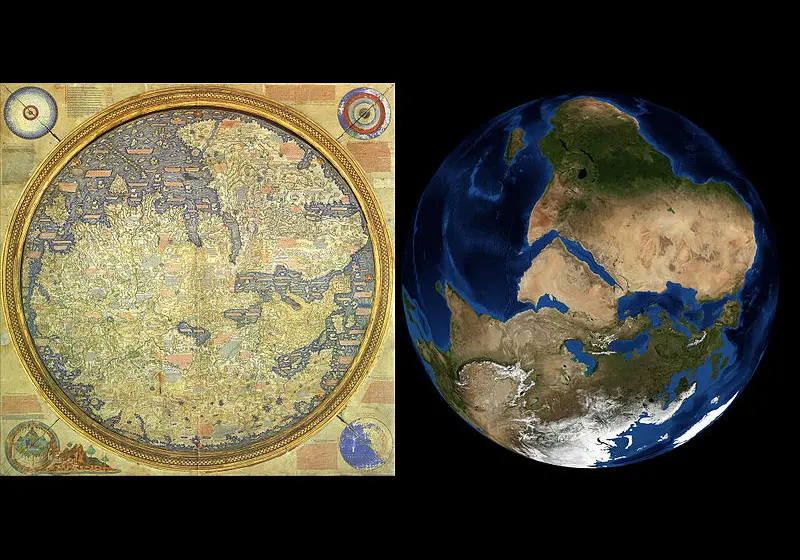

Comparing the world map in 1450 AD with NASA’s image of the Earth; Source: Wikimedia
Did you know about the evolution of the map throughout history? In your opinion, which stage has had a more revolutionary impact on the development of cartography skills? Please share your views with us and other Kajaro users.
Cover photo: Johnson Map; Photo source: Wikimedia; Cartographer: Alvin J. Johnson
Frequently asked questions
When does the oldest map of the world belong to?
A 25,000-year-old carved mammoth tusk in the Czech Republic appears to be the oldest known map.
What factors influenced the development of cartography during the Renaissance?
The advent of the printing press, the widespread publication of texts and maps, travel to distant places and the prosperity of sciences such as geography and astronomy were among the factors influencing the significant development of cartography skills during the Renaissance.
RCO NEWS

















