The interest rate is one of the most key factors that determine the path of investment and the value of assets in the economy and financial markets. This concept, although it seems simple on the surface, has a profound effect on the financial decisions of individuals, companies and even governments. You may think that the interest rate is only related to bank accounts and loans, but the fact is that this rate has the power to shake the entire world market, from stocks and commodities to digital currencies; For this reason, knowing and studying it is very important.
In recent years, with the dramatic growth of digital currencies and their increasing acceptance as an asset class, examining the relationship between interest rates and these emerging assets has become more important. Therefore, in this article we will examine what interest rates are and how they affect the crypto market.
What is the interest rate?
Interest Rate In fact, it is the amount and cost that is paid to borrow money. Central bankssuch as the Central Bank of America (Federal Reserve), this rate they determine And from that for control of the economy they use When the central bank lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper. This means that people and companies can borrow and spend money more easily. This will make the economy grow and economic activities will increase.
But if the economy grows too fast and prices rise too much (inflation), the central bank raises interest rates. Rising interest rates make it more expensive and harder to borrow, people borrow less and spend less money. This method helps reduce inflation and control prices.
Read more: What is the US interest rate? Introducing the best interest rate prediction sites
In simple words, the central bank regulates the growth rate of the economy by changing the interest rate; Just like reducing the flame under the pot!
How is the interest rate determined?
Determining the interest rate depends on various factors and is divided into two categories: short-term and long-term interest rates, which we explain below:
How is the short-term interest rate determined?
Short term interest rate by Central banks is determined The central bank tries to maintain price stability and liquidity balance in the economy by regulating monetary policies. The purpose of these policies is to prevent the money supply from increasing too much (which leads to inflation) or decreasing it too much (which causes recession).
Read more: What is inflation?
If policymakers want to reduce the money supply, they raise interest rates. This makes deposits more attractive and borrowing from banks less. Conversely, if they want to increase the money supply, they lower interest rates to make it easier for people and businesses to borrow and spend money.
How is the long-term interest rate determined?
The long-term interest rate is usually not dependent on the central bank’s cash rate and is mostly influenced by the yield of 10-year or 30-year treasury bonds. This yield is determined based on the demand in the market, after the auction of these bonds by the Ministry of Treasury. If the demand for these bonds is less, the interest rate will increase. But if the demand is high, the interest rate will decrease.
Long-term interest rates are effective for loans such as fixed-rate mortgages, auto loans, student loans, and some other long-term loans. In general, the long-term interest rate is lower than most short-term credit products, but is usually set higher than the prime rate.
How to predict possible interest rate changes
Predicting the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions can be challenging, but given some indicators and information, it is possible to speculate more reasonably. In the following, we explain the three important steps for predicting changes in the Federal Reserve interest rate:
Monitoring key economic indicators
The Federal Reserve considers several economic indicators to decide on interest rate changes. Some of the most important indicators include inflation, gross domestic product (GDP) growth, and the unemployment rate:
- Swelling: The goal of the Federal Reserve is to keep inflation at a manageable level. When inflation is higher than expected, interest rates are likely to rise to slow economic growth.
- GDP growth: If the economy grows faster than expected, the Federal Reserve may raise interest rates to prevent excessive demand and inflation. Conversely, if economic growth is slow, interest rates may be lowered to avoid recession.
- Unemployment: A low unemployment rate is usually a sign of a healthy economy. But if the unemployment rate falls too low, it can create inflationary pressure that forces the Federal Reserve to raise rates.
By following these indicators, one can understand how the Federal Reserve may react to economic conditions.
Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) follow-up
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meets regularly, although these meetings are held behind closed doors. But the Federal Reserve usually publishes the minutes of these meetings; It also holds press conferences to explain its policies. By reading these reports and announcements, investors can understand the Fed’s views on the economy and possible interest rate changes.
Looking at credible private sector forecasts
The forecasts provided by the private sector include the views of renowned economists and analysts who monitor the same indicators as the Federal Reserve. These forecasts can give you good information about the overall economic direction and help you predict what changes the Federal Reserve might make in its monetary policies.
By following these steps and information, you can have a better analysis of the decisions of the Federal Reserve and better predict the trend of interest rate changes.
How do interest rates affect other assets?
Interest rates can have many effects on various asset markets. In this section of the What is interest rate article, we examine how it affects some common assets:
- stock: Higher interest rates usually lead to lower stock prices. The price drop is because as interest rates rise, borrowing costs for companies rise. In other words, companies have to pay more to finance their projects; This issue can lead to a decrease in their profitability and reduce the attractiveness of the shares for investors.
- Bonds: When interest rates rise, the demand for newly issued high-interest bonds increases. At the same time, the price of existing bonds decreases; Because these bonds usually offer a lower interest rate than new bonds and therefore are less attractive to investors.
- Real estate: High interest rate means more expensive mortgage. An increase in the cost of mortgages reduces the demand for housing. This decrease in demand, in turn, can lead to a decrease in real estate prices; Because fewer people can afford to buy a house.
These effects show that the interest rate affects not only the digital currency market, but also many other financial markets.
The main types of interest rates
There are different types of interest rates, and understanding their difference can be a great help in understanding the economy:
- Fixed Interest Rate: A fixed interest rate is a rate that does not change throughout the loan period. For example, if you take out a loan with a fixed interest rate of 5%, your monthly repayment will always remain the same. This type of rate is common in home loans, personal loans, marriage loans, student loans, and car loans.
- Nominal Interest Rate: The nominal interest rate is the rate that is determined at the time of the loan or investment. This rate can be seen in advertisements and mortgage or car loan contracts. For example, if you borrow £100 at 6% interest, you will pay back £6 in interest. This rate is used in bonds and short-term loans.
- Prime Interest Rate: The prime interest rate is the lowest interest rate that banks offer to their highly creditable customers. This rate is usually used as a benchmark for other loans. For example, if the standard interest rate is 8 percent, someone with excellent credit may get a loan with an interest rate of 5 percent or less.
- Simple Interest Rate: It is a rate that is applied only to the principal amount of the loan and does not include interest compounding. For example, if you borrow £500 at a simple interest rate of 5%, you will repay a total of £525. This type of rate is common in credit cards.
- Annual Interest Rate: This rate includes interest compounded over a year. If the interest rate is 8% per annum, for a loan of £1,000, £840 will be repaid after one year.
- Effective Interest Rate: The effective interest rate is the rate that is paid in real terms after considering inflation and interest compounding. If the nominal interest rate is 7.95% and the inflation rate is 0.25%, the effective rate is approximately 8%.
- Fair Interest Rate: A fair interest rate includes all costs and fees associated with the loan; For example, if the fair rate is 8 percent, it includes the nominal interest rate, the effective rate, and fees. You should always check the terms and additional fees when taking out a loan.
- Variable Interest Rate: A variable interest rate changes over time and is usually tied to an index such as the LIBOR rate. This means your monthly payment may increase or decrease. This type of interest rate is more common in student loans.
Federal Reserve interest rates and their impact on digital currencies
The interest rate of the Federal Reserve is one of the determining factors in the behavior of financial markets, including the digital currency market. As the central bank of the United States, the Federal Reserve is responsible for managing interest rates, which have a direct impact on the cost of borrowing and the flow of money in the economy. The impact of interest rates on the digital currency market is especially evident when rates are low.
When interest rates are low, investors are more willing to invest in riskier assets such as cryptocurrencies to earn higher returns. This issue increases the demand and, as a result, increases the price of digital currencies. But as interest rates rise, safer assets such as bonds and savings accounts become more attractive and investors move towards these assets; which can reduce the price of digital currencies.
The trend of changing interest rates can also be seen in the history of the price of digital currencies, so that when prices fall sharply, liquidity leaves decentralized financial protocols or DeFi (DeFi) and blockchain ecosystems may become stagnant and inactive.
Read more: What is DiFi?
The relationship between interest rates and digital currencies
Although cryptocurrencies operate outside of the traditional banking system, changes in interest rates can greatly affect the cryptocurrency market. In the following, several main ways that interest rates affect this market have been examined:
Money flow and investment
Interest rates affect the rate of return on traditional investments such as bonds and savings accounts. When interest rates are low, investors tend to shift to riskier assets such as cryptocurrencies. In this situation, the demand for digital currencies increases. But when interest rates rise, investing in traditional assets becomes more attractive and demand for cryptocurrencies declines.
Read more: How to invest in digital currencies?
Willingness to take risks
Low interest rates make investors more willing to accept risk; Because the yield of safe investments is low. In such a situation, digital currencies become more attractive as high-risk assets, but with high return potential. But when interest rates rise, investors prefer to move to lower-risk, more stable-yielding assets such as bonds.
Read more: Getting to know the concept of risk and time horizon in investment
Liquidity and borrowing costs
Low interest rates make borrowing cheaper. In such a situation, traders may use credit to buy digital currencies. This can increase demand and, as a result, increase prices. But if interest rates rise, borrowing costs will rise and investors may borrow less; This can affect the price of digital currencies.
Inflation and devaluation
When inflation rises, central banks usually raise interest rates. In this situation, some investors seek to protect their capital against inflation and consider digital currencies, especially Bitcoin, as a risk hedge. This can increase the demand and price of digital currencies. However, if high interest rates can control inflation, the need to buy digital currencies will decrease; This may negatively affect prices and investors will move to bonds.
Read more: Can Bitcoin be a hedge against inflation?
Historical examples of the impact of interest rate changes on the digital currency market
To better understand how changes in interest rates can affect the cryptocurrency market, let’s take a look at some important historical periods that illustrate these effects.
Low interest rates after the 2008 financial crisis
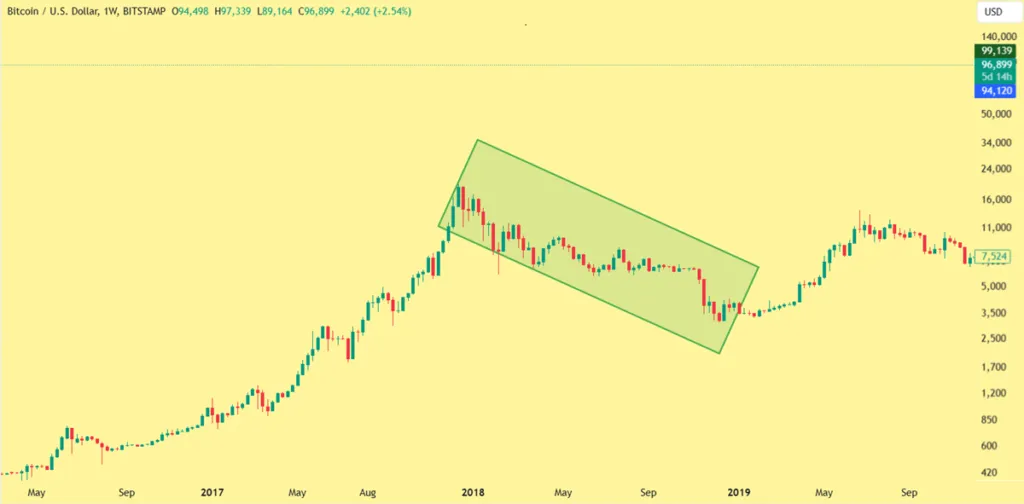
After the global financial crisis in 2008, central banks around the world decided to cut interest rates significantly to boost the economy and create conditions for recovery. These low interest rates caused returns on traditional investments such as bonds and savings accounts to drop sharply, and investors sought higher-yielding assets.
These conditions contributed to the birth of Bitcoin and the digital currency market; Because Bitcoin looked attractive as an anti-inflation asset and potential. For example, the price of Bitcoin went from less than $1 in 2009 to over $20,000 in late 2017. This significant increase in the price of digital currencies showed that investors paid more attention to these assets in the era of low interest rates.
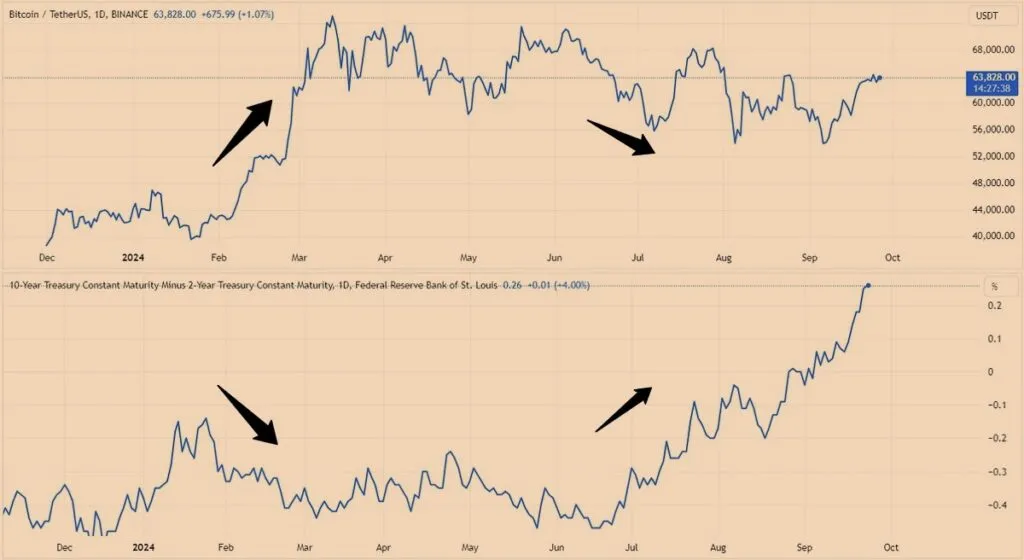
Federal Reserve interest rate hike in 2018-2017
The Federal Reserve gradually increased interest rates in 2017 due to economic growth in the United States and rising inflationary pressures. This contractionary monetary policy made traditional assets like bonds and savings accounts that offered higher returns more attractive to investors. Investors also gravitated towards these more stable assets, which reduced the appeal of digital currencies.
Accordingly, the digital currency market, which experienced a strong upward trend in 2017, saw a sharp price drop in 2018. For example, the price of Bitcoin fell from its high in late 2017 (nearly $20,000) to around $3,200 at the end of 2018. This period showed that changes in interest rates can greatly affect the digital currency market and cause prices to fall or rise.
Response to Corona and new monetary policies
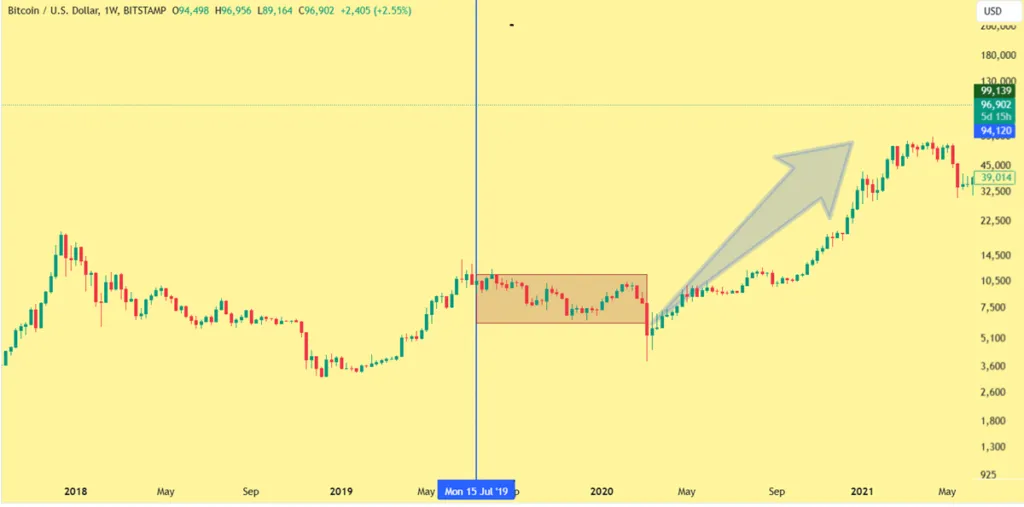
After the outbreak of the Corona virus in 2020, central banks around the world raised interest rates to near-zero levels in order to support the global economy and prevent recession. These policies, along with economic stimulus programs and increased liquidity, created conditions where investors sought higher-yielding assets. During this period, digital currencies became more attractive due to their high liquidity and special features such as limited supply.
Bitcoin and other digital currencies experienced significant growth during this time; Especially, Bitcoin reached more than 60,000 dollars from 5,000 dollars in 2020-2021. This growth showed the impact of the economic conditions caused by the Corona crisis and supportive monetary policies, which increased the demand for digital currencies.
summary
Interest rate is one of the most basic concepts in economics and finance, whose effects are felt in all aspects of the economic life of individuals and societies. This index affects not only loan and savings costs; Rather, it acts as a powerful tool in economic policies to control inflation, economic growth and financial stability.
The importance of interest rate goes beyond the traditional financial fields and is considered as a key indicator in economic decisions due to its role in guiding the behavior of investors and determining cash flow. Although digital currencies are somewhat independent of traditional financial systems due to their decentralized nature, evidence suggests that macroeconomic changes, such as changes in interest rates, continue to have an undeniable impact on this emerging market.
RCO NEWS

















