Unlike Bitcoin, whose supply is limited to 21 million units, the issuance of new Ethereum tokens has no ceiling. For a while, it seemed that Marj’s update had succeeded in turning Ethereum into an anti-inflationary asset; But now the annual inflation rate of this asset has become positive again.
According to CoinDesk, data from the website “ultrasound.money” shows that Ethereum’s net emission rate (annual inflation rate) has turned positive again, reaching 0, after turning negative amid the volatility caused by the collapse of the FTX exchange. 07% has increased. At that time, due to the increase in transactions on the Ethereum network, the rate of token burning had also increased and inflation had become more negative than before.
The current positive inflation rate, however, indicates that the volume of new ethereum being minted on the network is greater than the amount being burned on a regular basis. According to ultrasound.money data, the circulating supply of Ethereum has increased by 0.14% in the last seven days and on an annual basis.
Nick Hotz, vice president of research at digital asset management company Arca, believes that the lack of activity on the network has led to a decrease in demand, resulting in positive annual Ethereum inflation.
Hotz told CoinDesk:
Immediately after the FTX crisis and due to the fluctuations created in the market, there was a great demand for the exchange of assets in centralized and decentralized exchanges. In the following weeks, this subsided and now the demand for using centralized and decentralized exchanges is much reduced.
A large portion of market participants expected the big Merge update to permanently turn Ethereum’s annual inflation rate negative. It should be noted that with the update of Marj on September 15 (24 September), Ethereum’s proof-of-work protocol was changed to a proof-of-stake model with optimal energy consumption. On paper, Marj would reduce the issuance of new tokens by 90% by removing 1,600 Ether units per day, which was the reward for mining and staking in the network.
Also read: What are inflationary assets and anti-inflationary assets?
Of course, Ethereum’s inflation rate is also dependent on a separate mechanism called Ethereum Improvement Proposal “EIP-1559”. A mechanism that burns a portion of the fees paid for Ethereum transactions, or in other words removes it from the network cycle. The EIP-1559 plan basically depends on the amount of Ethereum burned from using the network. Therefore, the more transactions on the blockchain, the more Ethereum will be burned.
According to data from the website Etherscan, the amount of Ethereum burned every 24 hours increased by 500 Ethereum a day after the collapse of the FTX exchange, which caused volatility in the market. Now, however, this rate has dropped to around 1,200 Ethereum per day.
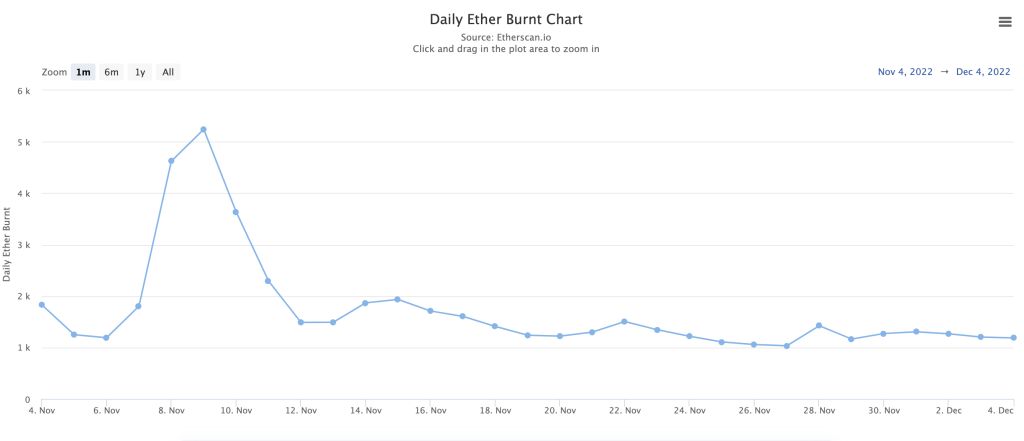
Hotz believes that this mechanism is neither completely inflationary nor completely anti-inflationary, but it creates a reliable and stable supply (inflation rate) of Ethereum, which will lead to greater adoption of Ethereum through Layer 2 networks.
He added:
This mechanism is very similar to what the Federal Reserve does with the US economy: when the economy is overheated, it reduces the money supply, and vice versa. This is what the EIP-1559 does. An idea that works well, especially after Marj.
At the time of publication of this report, the price of Ethereum has decreased by more than 3% in the last 24 hours and is trading in the range of $1,260.
RCO NEWS

















