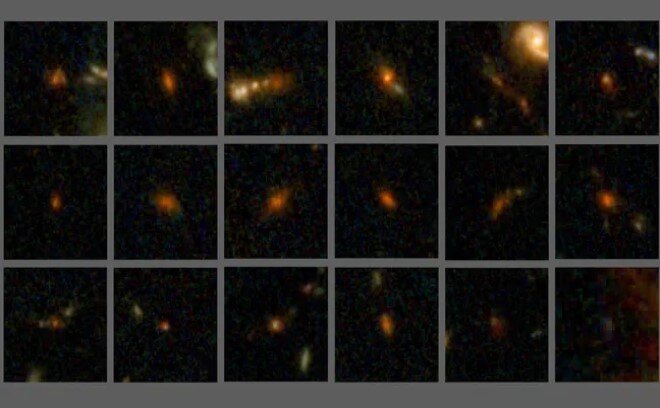
According to RCO News Agency, quoted by Space, a group of astronomers have succeeded in identifying galaxies that were formed less than a billion years after the Big Bang; A discovery that can change the human understanding of the process of galactic evolution.
These galaxies seem to be rich in “metals”; A term used by astronomers to describe elements heavier than hydrogen and helium. Meanwhile, current models predict that the formation and distribution of these elements occurred in the next generations of stars.
“Dusty galaxies are massive systems with large amounts of metals and cosmic dust,” University of Massachusetts Amherst researcher Jorg Zavala said in a statement. “These objects are very old and show that their stars were formed in the very early stages of the universe, contrary to the predictions of current models.”
This research began when Zavala and his colleagues identified about 400 bright and dusty galaxies using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) telescope, a set of 66 radio antennas in the Atacama desert in Chile.
Additional investigations using the James Webb Space Telescope narrowed the list down to 70 candidates for faint dusty galaxies at the edge of the universe; Many of which have never been seen before.
Next, by combining data from James Webb and ALMA, the researchers confirmed that some of these galaxies formed only 500 million years after the Big Bang. The finding not only challenges the existing narrative of cosmic history, but also suggests their possible connection to two other families of strange galaxies: the very bright, star-forming galaxies discovered in the early universe, and the older, “quiet” galaxies that no longer produce stars.
Zavala says about this: “It is as if we now have images of the life cycle of these rare galaxies; Super bright galaxies are young; Quiescent galaxies are in old age; And the galaxies we found are young but mature examples.”
However, more research is needed to accurately understand the relationship between these three groups. If this connection is confirmed, it will be a clear indication that a part of human knowledge about galactic evolution is still unknown and that the process of star formation may have started in the universe much earlier than previously thought.
RCO NEWS