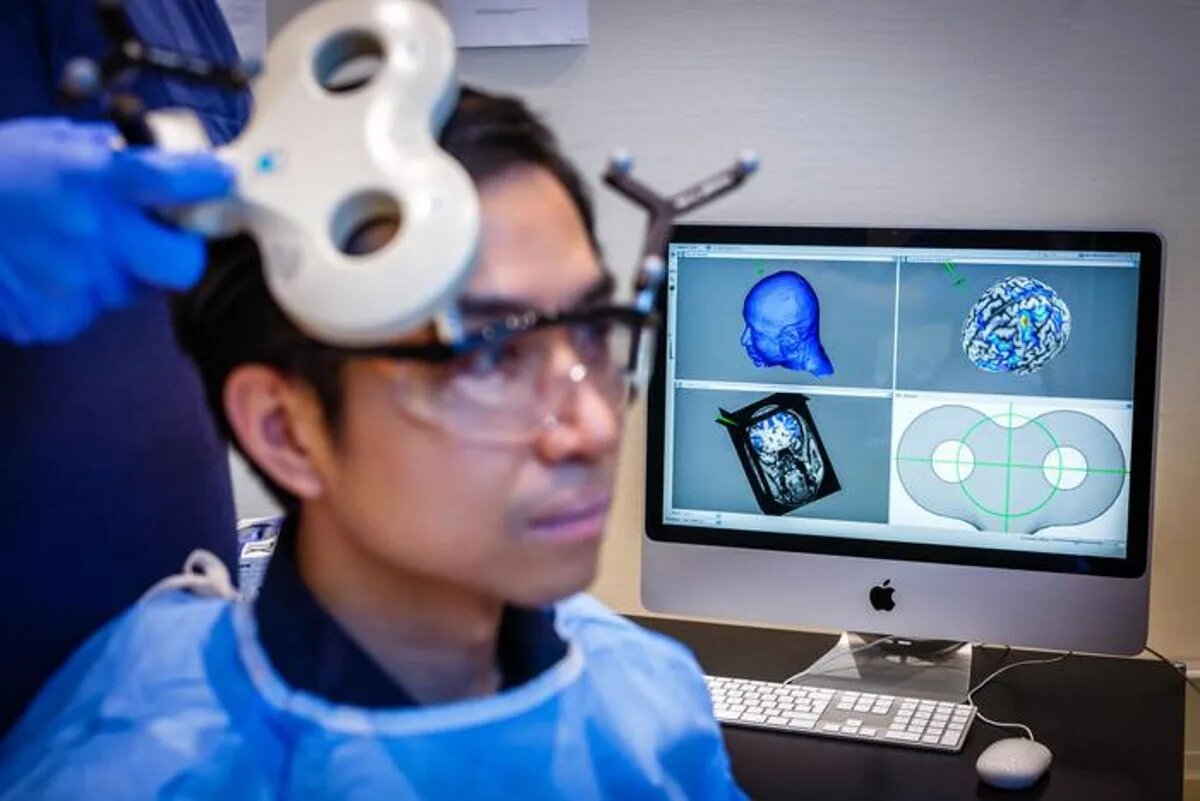
According to the Mehr news agency, quoted by Independent, researchers in an experiment in which electric current was used to stimulate two parts of the brain, were able to encourage people to share their money more. They believe that these findings show that altruism is institutionalized in our brain in such a way as to make us care for others, and in addition, it provides the basis for further research on cooperation.
In a new study conducted by the University of Zurich, 44 participants were asked to divide some money between themselves and unknown partners. While the participants were making decisions, the researchers stimulated the frontal lobes of their brains using electrical currents. This part of the brain plays an essential role in the sense of taste, hearing, sight, touch and smell.
This stimulation was adjusted to make the brain cells in these parts activate with a specific pattern with a gamma frequency between 40 and 90 Hz or an alpha frequency between 8 and 12 Hz.
According to the researchers, when a higher frequency was used for stimulation, participants were more likely to make an altruistic choice and give more money to another person. This trend was true even if they earned less money overall.
Ji Hu from East China Normal University and one of the authors of the research says about this: When we changed the communication in a specific brain network using non-invasive stimulation, people’s sharing decisions changed in a coordinated way and the way they used to balance themselves and others was transformed.
With this research, the researchers showed that the said stimulation process changed the person’s non-selfish preferences and caused them to consider their partner more when evaluating any financial offer.
RCO NEWS