Dr. Mehrangiz Rajabi and Dr. Elham Rajabi, a doctoral graduate of Amirkabir University of Technology, under the guidance of Dr. Kamran Dehghani, a member of the faculty of the university, launched a research project titled “Design and Construction of the New Alloy High TIZRNBMOV and Tizrnbmv”
Rajabi explained: Traditionally the Ti-6al-4V alloy is today considered the most common bone implantation, but there are always concerns about the abrasion and concentration of ions released by the body.
He emphasized: During the use of this traditional alloy, the release of toxic vanadium and aluminum ions around the tissue lead to diseases such as Alzheimer’s and neurological diseases, and said: In addition, the high amount of abrasion rates in artificial bonds can be another disadvantage of the traditional Ti-6al-4V alloy.
According to him; Due to the low abrasion resistance of the Ti-6al-4V alloy, wear-residual waste during service may also lead to tissue inflammation and other diseases.
“Given these constraints and problems of traditional alloys, recent new anthrop alloys, on the one hand, have been highly regarded because of their unique properties and because of their high biocompatibility as a replacement for common biomedics,” he said.
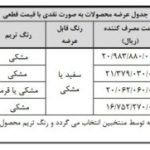
He noted: In this study, two new alloys of Tizrnbmov and Tizrnbmota were designed and manufactured using thermodynamic relationships and the use of simulation software to produce materials. Their biomass properties were then compared to the traditional Ti-6al-4V alloy. The results of tests on the new TI35NB25ZR15MO15MO15V10 showed that this alloys showed much higher corrosion resistance in different environments, especially in the simulator environment than the conventional Ti-6al implant. Also, the examination of cellular reproduction and life showed that the high TIZRNBMOV and Tizrnbmota alloys show a much higher biomass and have a very good replacement with the common Ti-6al-4V biomass.
Rajabi said another important parameter in the examination of metal planting properties is the elastic alloy modulus, which should not have a very high number of bones and continued: In general, the elastic modulus of orthopedic alloys is about 1 to 2 GPa. The high -term elastic modulus of the conventional alloys in the long run results in the effect of stress shields, resulting in impact and osteoporosis loosening. However, the elastic modulus of the new anthrop alloy is designed to be less than traditional planting and about 1-5 GB, indicating the high biomass of the new anthrop alloy.
He also added that the alloys’ abrasion behavior also showed that the alloy of Tizrnbmota’s entropy alloys showed a resistance of about 2 percent higher than the Ti-6al-4V. Therefore, the new designed alloy can be a very good alternative to the Ti-6al-4V alloy in medical engineering applications.
According to the researcher, high entropy alloys are a new group of alloys that, given their special properties, can be used for a wide range of applications, especially in medical engineering. The high entropy alloy we designed is aimed at using as a bone implant in medical engineering.
He added: “In general, the design and processing of the new TI35 NB25 ZR15MO15 V10 and Ti35 NB25 ZR15MO15 TA10 for medical and high -life use, which has not been studied so far, is one of the most important innovations of this project.”
(tagstotranslate) Implant (T) Amir Kabir University (T) Scientific Research
RCO NEWS