Our Milky Way Galaxy is the home of very strange phenomena. Now the discovery of a completely spherical mass in it has led to astonishing astronomers.
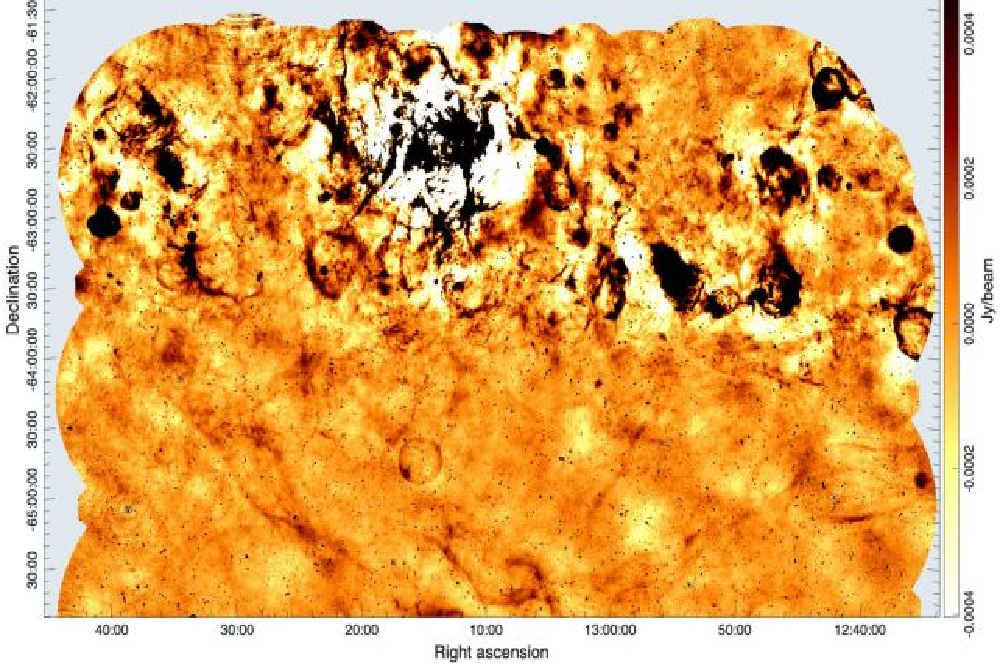
According to RCO News AgencyAstronomers have found a crime that seems to be a completely spherical bubble in the data collected by a powerful radio telescope. This spherical mass is a mass of expanding materials exploded by a star. This is the remains of a Supernova that has been thrown out. However, how it is formed is a puzzle.
According to Science Alert, a large international team led by Miroslav Filipović Astrophysics of the University of Western Sydney in Australia has called the crime “Teleios” which means “in Greece“. After thoroughly examining the possibilities, scientists have come to the conclusion that they need more information to understand how this crime is formed.
The Askap Telescope is discovering a treasure trove of “strange circles” (ORCS) of different types of sky to explore its “Gate Evolution Map” (EMU). It has been a bit difficult to understand the origin of some of the galactic intervals.
The teleios spherical mass, located in the Milky Way, has a different source of “strange radio circles” found deep in the universe, but even though it is closer and smaller, scientists’ inability to accurately determine its distance was a major obstacle to understanding its origin.
Filipovic and his colleagues conducted a thorough investigation into the crime and found that it only shines poorly during radio wavelengths. The wavelength of its luster showed that the remains of a “first supernova” (IA) are likely to be the remnants of a “IA). This type of “supernova” is one of the brightest types of “supernova” in the world.
These “supernovae” occur when a white dwarf is in a binary circuit close to a adjacent star, and the stars are so high that it goes beyond its mass and explodes.
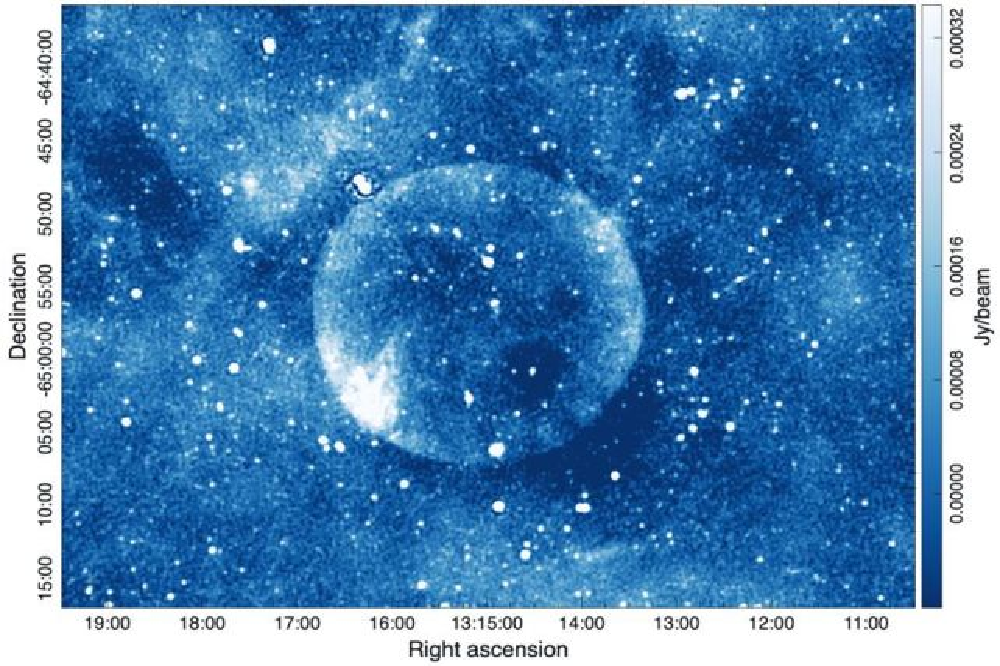
It is very difficult to determine the distance of objects in space. Researchers were able to obtain estimates for the “Teleios” distance, but failed to limit the estimation beyond two options. One option is about 7175 light -years and the other is about 25,114 light years.
Each of these intervals will have different meanings for the “Teleios” evolutionary history. Since the bodies are farther, they look smaller, these two gaps create very different sizes for this bubble. In the closer distance, the remnants of the “supernova” will be 46 light -years and will be 157 light -years away.
The remnants of “supernova” are often made up of an expanded cloud of materials, so each of these sizes represents a different age for these remains. The closer distance represents the younger remnants of “supernova”, which has been less than 1,000 years for growth and should be more than 10,000 years away.
The problem for both of these possibilities is that the evolutionary models of “first clouds” predict that X -rays should exist. The lack of X -rays is a bit confusing.
Another possibility is that “Teleios” will be the remnants of a supernova type “IAX”. This type of “supernova” is a new “first supernova” that does not completely destroy the white dwarf, but leaves the remains of a Zombie star. This is well in line with the “TeleiOS” launching features, but this spherical mass should be much closer to this.
This means that “Teleios” is a little smaller and is about 11 light years. There is even a star in the distance that can be a “zombie” star. But none of the other independent measurements from the “Teleios” distance shows that it can be so close.
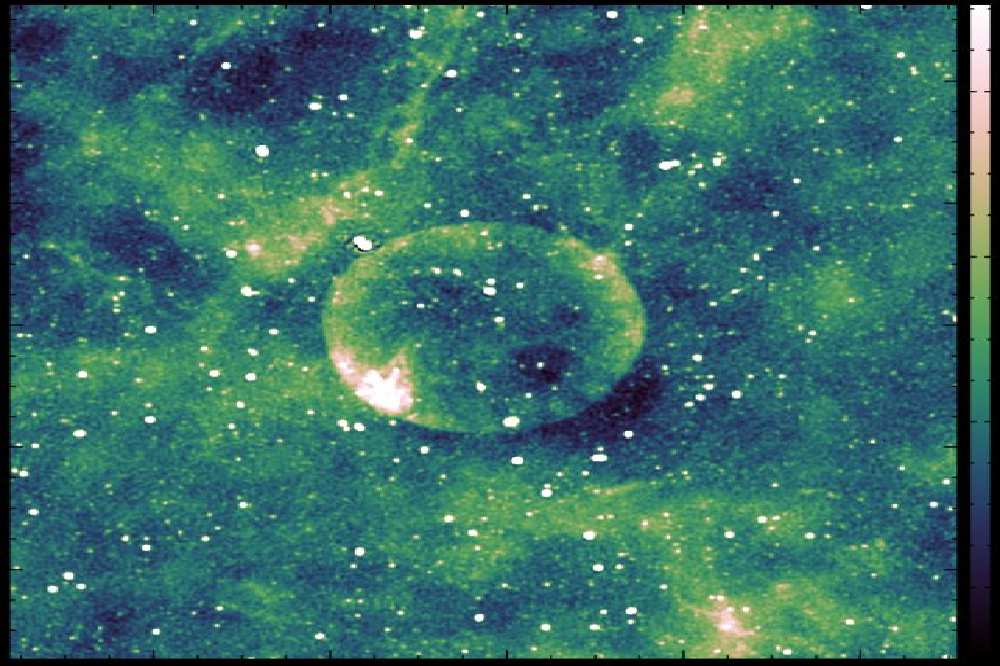

All of these issues make the remnants’ abnormalities an abnormal symmetry of the remains. The remnants of the “supernova” are almost always asymmetrical. The explosion alone may be asymmetric. Expanding materials may collide with the pre -exterior “interstellar” gas or dust, and eventually, the shell expands enough to begin fragits.
However, if the “supernova” is symmetrical and occurs in an empty area in space, it can be symmetrically expanded and may not only reach the fragmentation point. This is a scarce landscape, but it is not impossible. This is what makes Teleios really interesting.
Scientists say: “We have conducted a comprehensive examination of the potential” supernova “based on the level of surface brightness, appearance and possible intervals. All of the hypotheses raised face challenges, especially given the lack of a measurable X -ray, which must be recognizable based on our evolutionary modeling.
“We see the” first supernova scenario “as the most likely option, however, there is no direct evidence to confirm none of these possibilities, and new observations with high sensitivity and clarity are needed.
The study is published in the journal Astronomical Society of Australia.
The end of the message
(tagstotranslate) supernova
RCO NEWS