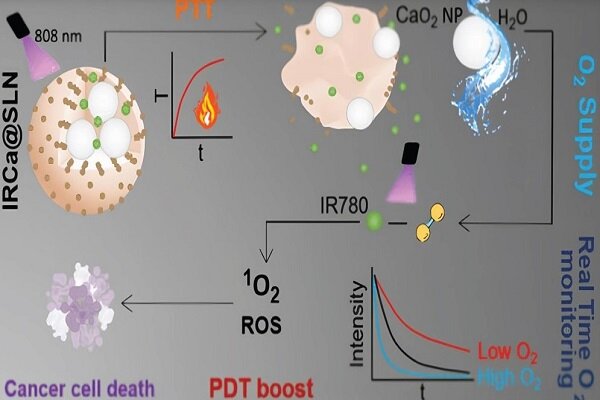
According to the report of Mehr news agency, citing the National Center of Genetic and Biological Resources of Iran affiliated with the Academic Jihad; A major problem with Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) for cancer treatment is “hypoxia” or lack of oxygen.
This problem is because the efficiency of photodynamic therapy is highly dependent on the presence of oxygen in the environment, because photodynamic therapy requires the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) to kill cancer cells, which are produced in the presence of oxygen.
In this research, to face this challenge, the first “solid oxygen-releasing nano-platform” that works in an oxygen-dependent manner has been introduced. This platform consists of IR780 and CaO2 nanoparticles that release oxygen in the presence of laser and improve the efficiency of photodynamic method in cancer treatment.
The efficiency of this method has been confirmed in tests performed on MDA-MB-231 cancer cells (a type of breast cancer cell).
The results showed that by using this method, the survival of cancer cells decreased significantly and the production of intracellular ROS increased significantly. This is despite the fact that without laser radiation and in the presence of the nanoplatform, no significant change in cell viability and production of reactive oxygen species was observed.
In other words, photodynamic effects are activated only in the presence of nanoparticles and laser radiation. These results show that the presence of CaO2 and IR780 nanoparticles in this nano platform improves photodynamic efficiency and effective response to light, and thus highlights this method as an effective tool in cancer treatment.
The results of this research have been published in the international journal ACS Applied Nano Materials. To read the mentioned article here click
RCO NEWS