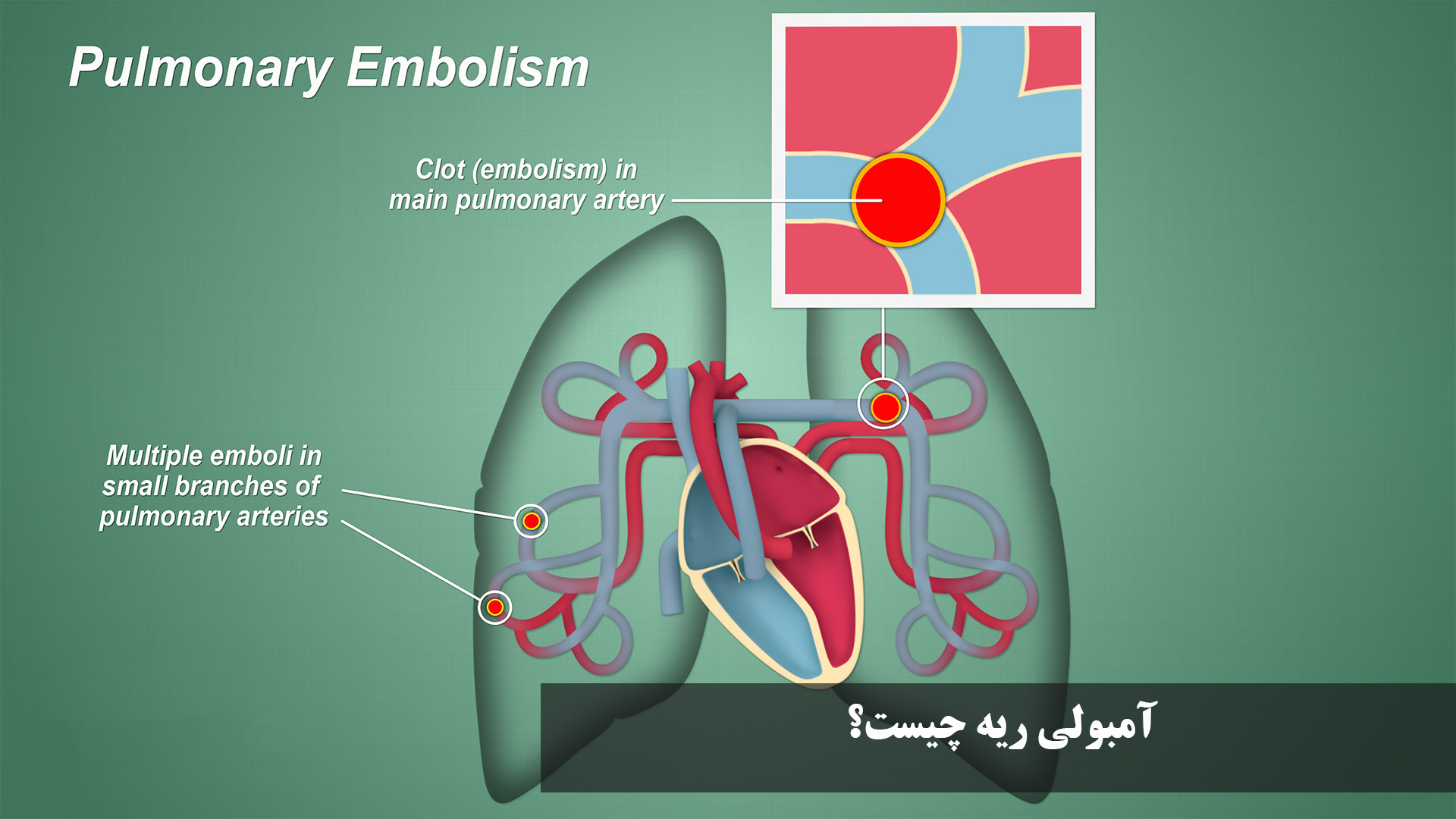
Lung embolism
Lung embolism is an important problem in the body that when it happens, blood flow to some of the lungs is blocked. This obstruction is usually due to the blood clot that moves from another part of the body (such as legs or pelvis) and enters the lung. When this clot closes the veins of the lungs, sufficient blood does not reach the lung tissue, which can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, cough or even threatening the patient’s life.
What is an article in Alamato today called Lung Ambolism? What causes lung embolism? Is there a definitive cure? We have brought you with us.
Also Read: What are the symptoms of lungs in the elderly?
What is a lung embolism?
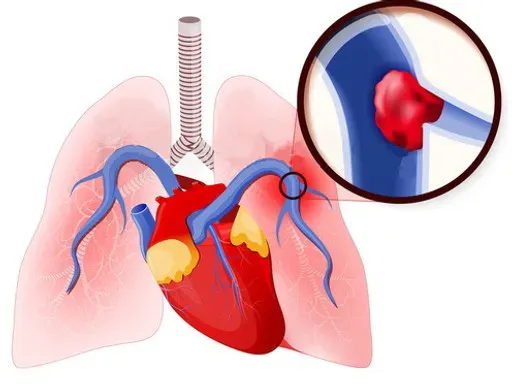
Lung embolism is a serious and sometimes dangerous disease that occurs when the lung is blocked by a substance such as blood clots, fat, tissue or even air bubbles. The most common cause is the blood clot, which is usually formed in the deep veins of the foot or pelvis (deep vein thrombosis) and then moved with blood flow and stuck in the lung veins. This obstruction causes the bloodstream to not reach part of the lung, lower blood oxygen levels and increase pressure on the heart.
Symptoms of lung embolism can range from sudden shortness of breath, chest pain and cough to milder symptoms such as heavy feeling or fatigue. In severe cases, if the clot is large, it can cause severe blood circulation and even death. In simple tongue, the lung embolism means the blood clot, which is the most common cause of the blood clot. The disease requires rapid diagnosis and immediate treatment to prevent its dangerous complications.
What causes lung embolism?
Lung embolism usually occurs due to blood clots in the deep veins of the foot or pelvis (deep venous thrombosis), which then moves to the lung and stuck in pulmonary arteries. Factors that increase the risk of blood clotting and consequently the incidence of lung embolism include three main categories: slowing blood flow (for example, in long rest in bed or long trips by car and plane), damage to the walls of the veins (following fractures, surgery or impact), and abnormal increase in blood clotting (due to inherited conditions).
Some important risk factors include: family history of embolism or thrombosis, heart disease such as heart failure, cancers (especially brain cancer, lung, ovarian, pancreatic and kidney cancer), obesity and overweight, pregnancy, taking some medications such as hormonal pills, protein deficiency, and enzymes. Older people and those with a low -life lifestyle are also more at risk. In addition to blood clots, sometimes other substances such as bone fracture fat, single tumors or even air bubbles can also cause lung arteries.
Also Read: The Best Antibiotic Pills and Ampoules for Lung Infection
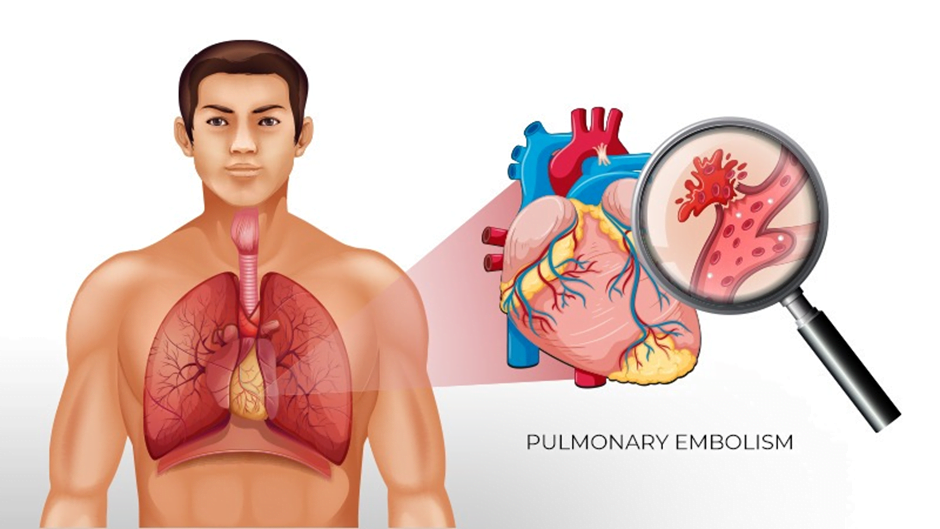

Does the lung embolism have a definitive cure?
Lung embolism is a serious illness, but fortunately it can be effectively controlled and treated by timely diagnosis and proper treatment. The principle of treating the disease is to prevent clotting and gradually dissolve it. For this purpose, blood thinners (anticoagulants) are commonly used. Medications such as warfarin have been prescribed for this purpose for many years, but today there are newer drugs such as apricasan and rivaroquesan that are highly effective and are easier for patients because they do not need to control blood tests.
In cases where the clot is very large and causes a serious risk to the patient, your doctor may use thrombolithic (clot soluble) or even surgery to remove the clot. Also under certain circumstances, a device called the IVC filter is placed in the large abdominal vein to prevent new clots from moving to the lung.
It should be noted that lung embolism is usually a long -term process and may require medication from several months to lifetime. Therefore, although lung embolism is controllable with treatment, prevention of re -clot formation and constant medical follow -up is an important part of the treatment process.
Also Read: What to eaten to clear the lung?

What to eat for the lung?
Foods useful:
- Green leafy vegetables such as spinach, broccoli and lettuce (Vitamin K source and blood circulation)
- Fatty fish such as salmon, tuna and sardines (omega -3 and anti -inflammatory)
- Fresh fruits, especially berries, oranges and pomegranates (rich in antioxidants)
- Whole grains such as whole grain bread, oatmeal and brown rice (to improve heart and veins health)
- Healthy water and liquids such as plain water, herbal demon and green tea (to keep blood dilute and prevent blood concentrations)
Foods that should be restricted or avoided:
- Processed foods such as sausages, sausages and fast food (high fat and salt)
- Saturated fats such as butter, solid oils and high -fat meats
- Sugar and alcoholic beverages such as drinks and alcohol (harmful to cardiovascular)
Important: Healthy cooking methods such as steaming, cooking and cooking in the oven are recommended. Frying foods should be aside as far as possible.
Also Read: The Best Demonous for Smoking Lungs
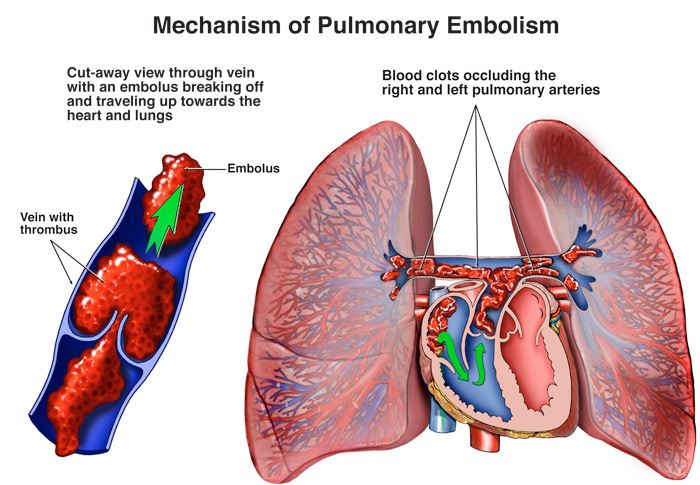

What is the length of the lung embolism treatment?
The duration of treatment of lung embolism depends on the condition of each patient and the severity of the disease. Typically, the use of blood thinners (anticoagulants) is recommended for at least 6 months. However, depending on the location and size of the clot, the cause of the patient and the general condition of the patient, the physician may continue the treatment for a longer period. In some people who have a specific disease or high risk of re -clot, medications should continue to continue even lifetime.
The exact duration of treatment is only possible by a specialist physician, and patients should take the medication as directed or arbitrarily, as early discontinuation of the drug can increase the risk of clot return and serious complications.

Complications after the treatment of lung embolism
Sometimes after the successful treatment of lung embolism, symptoms such as chronic shortness of breath or premature fatigue may still remain. In some cases, the clots are not completely absorbed and become scarred or wounded in the lung veins, which may cause chronic pulmonary blood pressure. Another complication is the recurrence of clotting or new clot, meaning that the clot is re -established in the veins, and the embolism is more likely to occur. Do not observe or the person is injured or hit.
In addition, some patients may be faced with reduced respiratory power and restriction in physical activity, meaning that after treatment they may no longer exercise or move easily as before.
Also Read: What to eaten to cope with air pollution?

The last word
In this post we have tried to give you all the information about lungs.
RCO NEWS
RCO