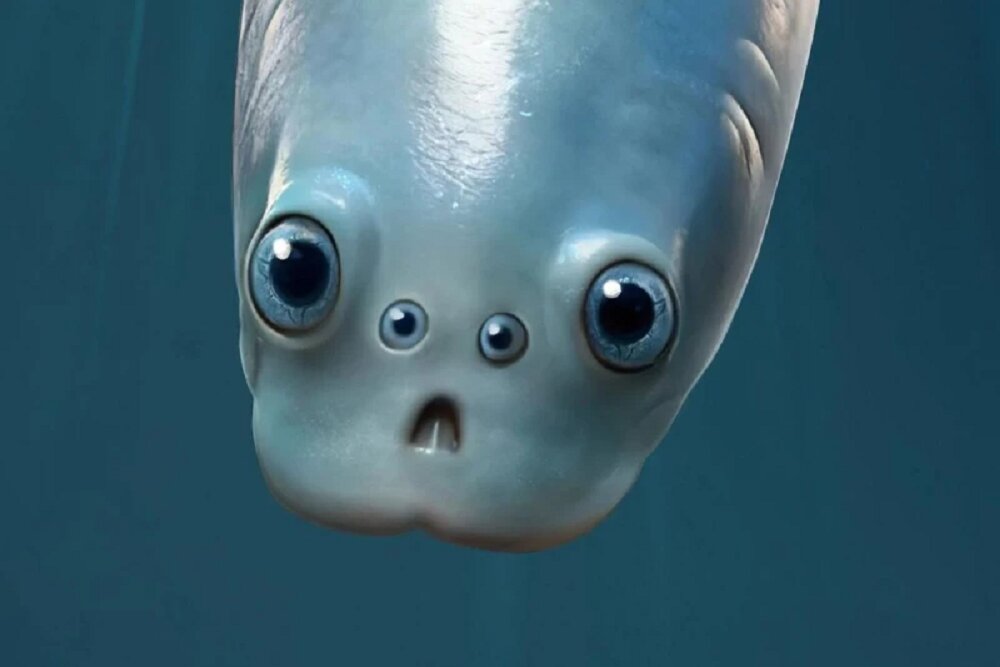
The earliest ancestors of all animals that had a backbone may have seen the world with four eyes, not just two. The remnants of those extra eyes are still present in the human brain in the form of pineal organs; A structure deep in the brain regulates our sleep cycle, but it no longer forms images.
According to RCO News Agency, “Early vertebrates had eyes like ours, but not just like us,” explained study co-author Jakob Winter from the University of Bristol. They had four eyes. He added: It is really amazing to think that our ancestors were swimming in the ocean about half a billion years ago and saw the world with four eyes. They probably had a much wider field of vision.
According to New Atlas, the Kunming region in China is famous for its exceptional preservation of fossil deposits from the early Cambrian period. There, Sihang Zhang and Pei Yun Kong found specimens of two species of mylloconmingids, which represent the first vertebrates. Both species, which date back to about 518 million years ago, had exceptionally preserved four black spots on the front of the body: two larger spots on the sides of the head interpreted as eyes, and a second pair above and between them.
Researchers previously believed that the second middle pair are nasal capsules. However, this was an annoying inconsistency because we know that early vertebrates had only one nostril at the time. Under the electron microscope, the research group found the presence of melanosomes; Small packages that contain melanin. Melanin determines eye color and also absorbs light to create an image.
Before this fossil, the oldest fossilized melanin was from the Carboniferous period, about 300 million years ago. The fossils are “exciting because they show that we have preserved melanin that goes back a long time,” Winter says.
The researchers also found traces of a lens inside these organs. This scientist says: So they were really like eyes. This means that the beast had two large eyes on the sides and two small eyes on top, and both of them were camera eyes.
The paper suggests that our ancestors were at the bottom of the food chain and that four eyes probably evolved amid the environmental pressures of the Cambrian period. Having the ability to recognize more of the surrounding environment and a larger viewing angle is an advantage for escaping predators.
Over time, the ecological niche changed from refined feeders to carnivores, and the second pair of eyes may have evolved as a non-sensory neuroendocrine organ called the pineal gland; A structure that is responsible for producing melatonin and regulating the sleep cycle.
end of message
RCO NEWS