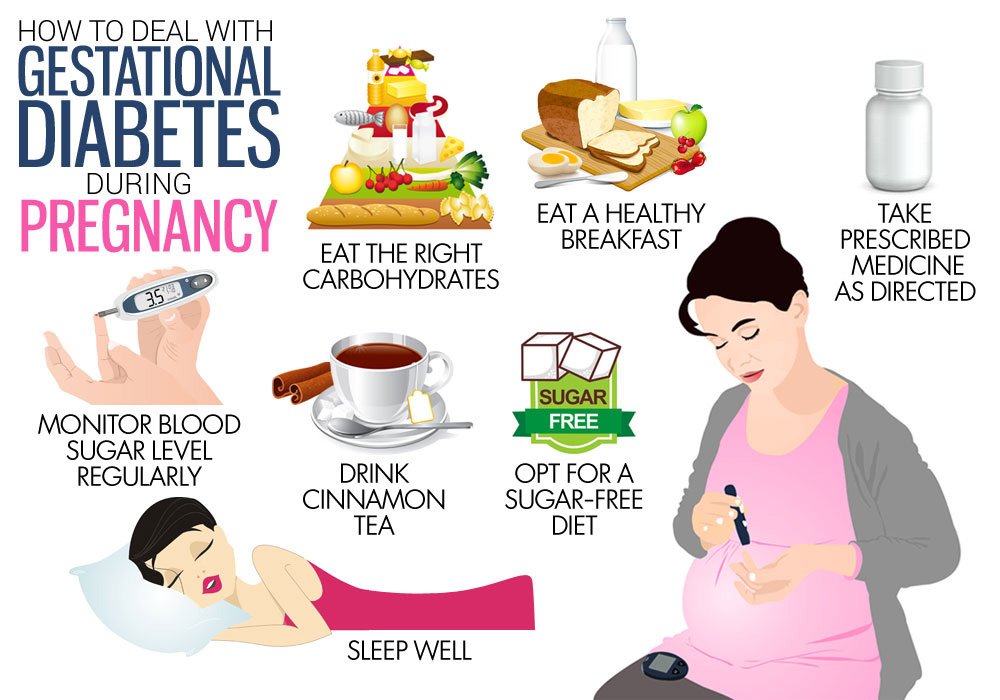
Pregnancy sugar
Pregnancy diabetes is one of the most common problems during pregnancy that usually occurs in the middle months to the end of pregnancy. In these conditions, the mother’s body cannot control blood sugar well and the blood sugar levels are above normal. Although this problem is often resolved after delivery, it can be dangerous to both the mother and the fetus if not controlled. For this reason, it is important to be aware of the amount of natural blood sugar in pregnancy and to identify its potential complications.
How dangerous is it in Alamato today? What are the complications of gestational diabetes on the fetus and the mother? We have brought you with us.
Also Read: How does vaginal discharge start in the first days of pregnancy?
High sugar complications in pregnancy for the fetus
Pregnancy diabetes and increased blood sugar in the mother not only affect maternal health, but also cause serious risks because the fetus receives its nutrients from the mother’s blood and excess sugar is stored in fat. This condition can cause abnormal enlargement of the fetus and problems during childbirth.
Other complications of pregnancy diabetes on the fetus include infant blood sugar (hypoglycemia), jaundice, premature birth, macrosomia (over 2 grams), increased risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes in adulthood, congenital defects in the heart, blood vessels, brain, spine, and kidneys. Proper control of blood sugar during pregnancy can reduce many of these complications and ensure the health of maternal and baby.
Complications of gestational diabetes on the mother
Pregnancy diabetes can affect maternal health during pregnancy and even postpartum. Although most maternal blood sugar returns to normal after childbirth, the likelihood of type 2 diabetes or pregnancy diabetes increases in subsequent pregnancies. Having a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise and proper diet can reduce this risk.
During pregnancy, diabetes makes the fetus enlargement, which can increase the likelihood of painful childbirth and stress for the baby. Complications of pregnancy diabetes for the mother include increased risk of cesarean section, abortion, hypertension or preeclampsia (pregnancy poisoning), polyhydraminius (excessive amniotic fluid in the uterus), premature birth and even death. Control of blood sugar, diet, and regular medical follow -up can reduce many of these complications and maintain maternal and fetal health.
Also Read: What is the cause of heart palpitations in pregnancy? Dangerous?


Fasting sugar in pregnancy should be how many
To perform pregnancy blood sugar tests, the person should be fasting between 1 and 2 hours, but drinking water is permitted during this time. In this experiment, a fasting blood sample is first taken, then the patient consumes sweet syrup or glucose, and after one and two hours of re -sampling. The experiment shows how the body manages blood sugar and, shortly after glucose consumption, the blood sugar levels rise and then returns to normal.
Interpretation of fasting sugar results in pregnancy:
- Fasting sugar is 2 mg / dL or less normal.
- Fasting sugar between 1 and 2 mg / dL means pre -diabetes and requires control of diet and exercise.
- Fasting sugar 2 mg / dL indicates gestational diabetes and treatment is required.
How dangerous is pregnancy?
During pregnancy, blood sugar above standard areas can be dangerous. Is exactly as follows:
Fasting (before breakfast): Blood glucose above 5 mg / dL is dangerous and indicates gestational diabetes.
One hour after eating 2 grams of glucose: sugar is above 5 mg / dL abnormal; Over 2 mg is severe and dangerous.
Two hours after eating 2 grams of glucose: Sugar above 2 mg / dL is abnormal and dangerous.
If your sugar is higher than these values, you should immediately be monitored by a physician because it has serious risks for the mother and fetus, such as excessive fetal growth, severe delivery, hypertension and the likelihood of type 2 diabetes in the future.
Also Read: Abdominal size and fetal movements in week 26 pregnancy


How many pregnancy sugar is they insulin?
Pregnancy diabetes is a condition that is above normal during pregnancy and requires accurate control to maintain maternal and fetal health. The decision to inject insulin is usually based on blood sugar levels and your doctor’s opinion. If the fasting sugar is above 2 mg or 2 hours after a meal is over 1 to 2 mg / dL and does not go down with diet and exercise, your doctor may prescribe insulin.
Insulin injection is necessary when blood sugar is constantly beyond the target range, as high sugar can cause problems such as high fetal growth, preterm labor or baby respiratory problems. By constantly examining the blood sugar and the status of the mother and fetus, the doctor decides whether insulin is needed, so regular tests and consulting with the specialist are important.
Normal blood sugar levels after breakfast in pregnancy
During pregnancy, blood sugar after breakfast (two hours after meals) should usually be less than 1 to 2 mg / dL. This area helps prevent problems such as high fetal growth, preterm labor or other complications.
If your blood sugar is higher and is not controlled by diet or exercise, your doctor may suggest a change in diet, physical activity, or even insulin use. Regular examination of blood sugar and consultation with a physician is essential to maintain the health of the mother and fetus.
Also Read: What is the Symptom Symptom Pelvic Pain in Pregnancy?

Blood glucose lower foods in pregnancy
To control blood sugar during pregnancy, it is best to include the following:
- Non -inscription Vegetables: Low calories, full of fiber that slow down the absorption of sugar and help control blood sugar. Such as chili peppers, spinach, broccoli, glycoom, cucumber, mushroom, zucchini, eggplant, celery, onions and lettuce.
- Lean Protein: Creates a feeling of satiety and provides essentials for fetal growth. Includes chicken, turkey, eggs, salmon, lean red meat, low -fat dairy and legumes such as beans and lentils.
- Healthy carbohydrates: Provide the body with the necessary energy and it is best to use low sources of glycemic index, such as brown rice, kinoa, breeze, sweet potatoes, whole grain bread and fresh or dried fruits.
- Healthy fats: They are useful for heart health and satiety, including avocado, nutrients, nuts and olive oil.
Forbidden or limited foods:
- Sweets and drinks containing added sugar such as cakes, biscuits, industrial juices and beverages.
- Starchy foods with high glycemic index such as white potatoes, white bread, white rice and pasta without bran.
- Processed foods containing hidden carbohydrates such as ready -made sauces, fast food and soaked potatoes.
Important Tips:
- Eat meals regularly and do not remove meals.
- Check the effect of foods and exercise with a blood glucose test.
- Choose low -fat, low -sugar, low -salt and low -calorie foods.
- Drink enough water and use fruits and vegetables instead of unhealthy foods.
- Take a daily basis and exercise with your doctor’s consultation.
- Weight control and regular follow -up of blood sugar are essential for maternal and fetal health.
Also Read: First Month of Pregnancy for Fetal Beauty


The last word
In this post, we tried to make it completely and comprehensive about sugar in pregnancy.
RCO NEWS
RCO